* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH 12-3 Power Point
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
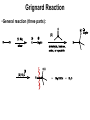
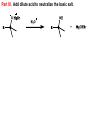
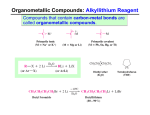
CH 12-3: Grignard Reaction-I •Important multi-step synthesis for making new C-C bonds, and 1o, 2o, and 3o alcohols. •The 3-step series of reactions includes the unique reaction of an alkyl halide (R-X) with magnesium metal (Mg) to form a C-Mg “organic-metallic” bond: •The “Grignard Reagent” is essentially a carbon nucleophile in the form of a coordinate covalent bond. •The Grignard Reagent then reacts with an oxygen compound (aldehyde, ketone, ester, epoxide) to produce a new C-C bond and an alcohol. Grignard Reaction •General reaction (three parts): Grignard Reaction – Step by step Part I. For carbon to be a nucleophile it must be activated by forming an organometallic compound (Grignard Reagent). X C 1o, 2o, 3o X C X C vinyl halide phenyl halide Alkyl halides react with Mg metal in ether solvent to form the “Grignard Reagent” containing a coordinate covalent bond. The metal stabilizes the carbon-anion. Part II. The Grignard reagent is: (1) a strong base (2) a good nucleophile The key reaction is addition to electrophilic C-O compounds to form alcohols: Grignard reagent Part III. Add dilute acid to neutralize the basic salt.