* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL FLIP NOTES - blog part 1
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
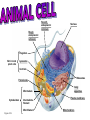
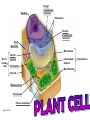
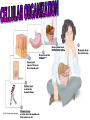
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Nucleus Rough endoplasmic reticulum Flagellum Not in most plant cells Lysosome Centriole Ribosomes Peroxisome Microtubule Cytoskeleton Intermediate filament Microfilament Figure 4.5A Golgi apparatus Plasma membrane Mitochondrion Nucleus Rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Microtubule Not in animal cells Central vacuole Intermediate filament Chloroplast Microfilament Cell wall Mitochondrion Peroxisome Plasma membrane Figure 4.5B Cytoskeleton Proposed in 1838 by Schleiden & Schwann 1. All life forms are made from one or more cells. 2.Cells only arise from pre-existing cells. 3.The cell is the smallest form of life. Body system level: the digestive system Organ level: the stomach Tissue level: layers of tissue in the stomach wall Cellular level: a cell in the stomach lining Chemical level: a molecule in the membrane that encloses a cell Organism level: the whole body • NO NUCLEUS • Small, simple • A prokaryotic cell is enclosed by a plasma membrane and is usually encased in a rigid cell wall –The cell wall may be covered by a sticky capsule –Inside the cell are its DNA and other parts • Grow & reproduce •EX. E. coli (bacterial cells) •HAVE A NUCLEUS & MEMBRANE-BOUND ORGANELLES •Grow & reproduce •Some live as single cells •Examples: Plants, animals, fungi, etc. Function: provide support and protection for the cell; allows water, oxygen, carbon dioxide and other things to pass through FOUND ONLY IN PLANT CELLS Function: controls most cell processes an contains hereditary info of DNA; has chromatin which forms chromosomes during mitosis Location: near the center of the cell Found in all EUKARYOTIC cells Function: Location where ribosomes are made Location: WITHIN the nucleus. Found in all EUKARYOTIC cells Description: DNA bound to proteins that is visible within the nucleus Location: WITHIN the nucleus. Description: Condensed chromatin, distinct, thread-like structures containing genetic information. Location: WITHIN the nucleus. Found in all EUKARYOTIC cells