* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download September 21 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
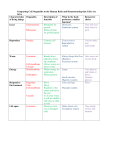
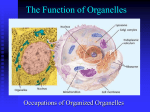
AP Biology John D. O’Bryant School of Mathematics and Science September 21, 2012 AP Biology Agenda Do Now (Quiz) Gifted, Young and Neglected Cells and Organelles AP Biology Lecture/Discussion Video clip: Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Membrane Video clip: Organelles in the Cytoplasm Do Now (Quiz) 1. Which of the following is a reasonable explanation for why unsaturated fatty acids help keep any membrane more fluid at lower temperatures? A) The double bonds form kinks in the fatty acid tails, forcing adjacent lipids to be further apart. B) Unsaturated fatty acids have a higher cholesterol content and therefore more cholesterol in membranes. C) Unsaturated fatty acids permit more water in the interior of the membrane. D) The double bonds block interaction among the hydrophilic head groups of the lipids. E) The double bonds result in shorter fatty acid tails and thinner membranes. AP Biology Do Now (Quiz) 2. Which of the following is a major cause of the size limits for certain types of cells? A) the evolution of larger cells after the evolution of smaller cells B) the difference in plasma membranes between prokaryotes and eukaryotes C) the evolution of eukaryotes after the evolution of prokaryotes D) the need for a surface area of sufficient area to allow the cell's function E) the observation that longer cells usually have greater cell volume AP Biology Do Now (Quiz) 3. A mycoplasma is an organism with a diameter between 0.1 and 1.0 µm. What does its size tell you about how it might be classified? A) It must be a single celled protist. B) It must be a single celled fungus. C) It could be almost any typical bacterium. D) It could be a typical virus. E) It could be a very small bacterium. AP Biology Do Now (Quiz) 4. In animal cells, hydrolytic enzymes are packaged to prevent general destruction of cellular components. Which of the following organelles functions in this compartmentalization? A) chloroplast B) lysosome C) central vacuole D) peroxisome E) glyoxysome AP Biology Do Now (Quiz) 5. Which of the following is a compartment that often takes up much of the volume of a plant cell? A) lysosome B) vacuole C) mitochondrion D) Golgi apparatus E) peroxisome AP Biology Do Now (Quiz) 6. Which is one of the main energy transformers of cells? A) lysosome B) vacuole C) mitochondrion D) Golgi apparatus E) peroxisome AP Biology Do Now (Quiz) 7. Grana, thylakoids, and stroma are all components found in A) vacuoles. B) chloroplasts. C) mitochondria. D) lysosomes. E) nuclei. AP Biology Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life’s Work AP Biology 2009- Food & water storage food vacuole plant cells central vacuole animal cells AP Biology contractile vacuole cytoplasm jelly-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes AP Biology signals Function Lysosomes digest food used to make energy clean up & recycle digest broken organelles Structure lysosomes small food particle vacuole digesting food AP Biology membrane sac of digestive enzymes digesting broken organelles A Job for Lysosomes 6 weeks 15 weeks AP Biology cytoplasm jelly-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes AP Biology signals lysosome food digestion garbage disposal & recycling Mitochondria Function make ATP energy from cellular respiration sugar + O2 ATP fuels the work of life Structure double membrane in both animal & plant cells AP Biology ATP cytoplasm jelly-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage mitochondria make ATP energy from sugar + O2 cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes AP Biology signals lysosome food digestion garbage disposal & recycling Plants make energy two ways! Mitochondria ATP make energy from sugar + O2 cellular respiration sugar + O2 ATP Chloroplasts make energy + sugar from sunlight photosynthesis sunlight + CO2 ATP & sugar ATP = active energy sugar = stored energy AP Biology build leaves & roots & fruit out of the sugars sugar ATP Mitochondria are in both cells!! animal cells plant cells mitochondria AP Biology chloroplast cytoplasm jelly-like material around organelles central vacuole storage: food, water or waste cell wall support mitochondria make ATP in cellular respiration cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals AP Biology chloroplast make ATP & sugars in photosynthesis lysosome digestion & clean up 2. Cells need workers = proteins! Making proteins to run daily life & growth, the cell must… read genes (DNA) build proteins structural proteins (muscle fibers, hair, skin, claws) enzymes (speed up chemical reactions) signals (hormones) & receptors organelles that do this work… AP Biology nucleus ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Golgi apparatus Proteins do all the work! one of the major job of cells is to make proteins, because… proteins do all the work! structural enzymes signals receptors DNA AP Biology proteins cells Nucleus Function control center of cell protects DNA instructions for building proteins Structure nuclear membrane nucleolus ribosome factory chromosomes DNA AP Biology cytoplasm jelly-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage lysosome food digestion garbage disposal & recycling nucleolus produces ribosomes nucleus protects DNA controls cell chromosomes DNA mitochondria make ATP energy from sugar + O2 cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes AP Biology signals Ribosomes Function protein factories read instructions to build proteins from DNA Structure some free in cytoplasm some attached to ER Ribosomes on ER AP Biology cytoplasm jelly-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage mitochondria make ATP energy from sugar + O2 cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes AP Biology signals lysosome food digestion garbage disposal & recycling nucleolus produces ribosomes nucleus protects DNA controls cell ribosomes build proteins Endoplasmic Reticulum Function works on proteins helps complete the proteins after ribosome builds them makes membranes Structure rough ER ribosomes attached works on proteins smooth ER makes membranes AP Biology cytoplasm jelly-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage lysosome food digestion garbage disposal & recycling ribosomes builds proteins mitochondria make ATP energy from sugar + O2 cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes AP Biology signals nucleus protects DNA controls cell ER works on proteins makes membranes Golgi Apparatus Function finishes, sorts, labels & ships proteins like UPS headquarters shipping & receiving department ships proteins in vesicles “UPS trucks” Structure AP Biology vesicles carrying proteins membrane sacs transport vesicles cytoplasm jelly-like material holding organelles in place vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage lysosome food digestion garbage disposal & recycling ribosomes builds proteins mitochondria make ATP energy from sugar + O2 cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals AP Biology nucleus protects DNA controls cell ER helps finish proteins makes membranes Golgi apparatus finishes, packages & ships proteins endoplasmic reticulum nucleus protein on its way! DNA RNA vesicle TO: TO: TO: vesicle ribosomes TO: finished protein protein Golgi apparatus Making Proteins AP Biology End 9/21 AP Biology