* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organization
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
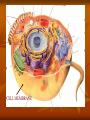
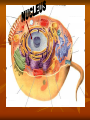
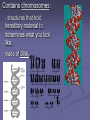
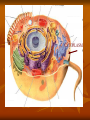
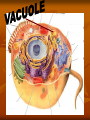
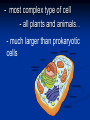
CHAPTER 2 cells P. 38 - 44 EARLY DISCOVERIES Anton Van Leeuwenhoek - made microscopes. - saw “critters” in a drop of water never seen before. Robert Hooke - first to see cells in slices of cork - ‘named’ cells. Led to others studying cells. Matthias Schleiden - studied every part of plants. - concluded all plant parts were made of cells. Theodor Schwann - studied animals. - concluded that all animals were made of cells. Rudolph Virchow - new cells come from other living cells. These scientists’ work led to the Cell Theory. Cell theory 1. 2. 3. All organisms are made of cells. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all organisms. All cells come from other cells. Read p. 38 - middle p. 42. STRUCTURE OF CELLS (p. 38) Scientists discovered there were parts inside the cell. A) Cell Membrane Like the protective skin of the cell - the outer covering. - controls what goes in and out. Food , water, oxygen enter - Wastes leave. Selectively permeable: controls what enters and leaves CELL MEMBRANE B) Nucleus the ‘control center’. B1) nuclear membrane -controls what goes in and out of the nucleus. - Contains chromosomes: - structures that hold hereditary material to determines what you look like. - made of DNA. C) Cytoplasm Found inside the cell membrane outside the nucleus. Gel - like substance: mostly water. Contains small structures called organelles -all have a “job” inside the cell. CYTOPLASM Cell Organelles Cells work 24 hours a day, 7 days a week Cell Organelle: working parts of the cell. Cell Organelles 1. Mitochondria Powerhouse of cell Food broken down and energy is released. Which cells might have lots of mitochondria? 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum (E.R.) Folded membrane Like conveyer belts in the factory. (or a highway) Transports materials throughout the cell. 3. Ribosomes Most numerous organelle in the cell Some attached to E.R. Produces protein (food) for the cell - releases energy from food. Which cells might have the most ribosomes? 4. Lysosomes - contains chemicals (enzymes) to digest wastes and ‘worn out’ parts of the cell. - called ‘suicide sacs’ - break open and digest the cell when it dies. 5. Vacuole Storage sacs Hold food, water, and wastes Larger in plant cells 6. Golgi Bodies -packages and secretes substances to the outer parts of the cell ASSIGNMENT: WORKSHEET “CELL STRUCTURE”. COLORED PENCILS NEEDED TOMORROW! PLANT CELLS -have two different parts than animal cells. 1. Cell Wall - found outside the cell membrane. - for support and protection. - non-living 2. Chloroplasts - where photosynthesis takes place (turns sunlight into food). - contains chlorophyll. (green) Two basic types of cells 1) Prokaryotic cells - oldest on Earth - no membranes around internal structures - (no nucleus) - very small - simplest type of cell ex. Bacteria ‘pond scum’ 2) Eukaryotic cells - organelles surrounded by a membrane. - has a nucleus - most complex type of cell - all plants and animals… - much larger than prokaryotic cells