* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
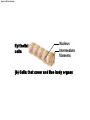
Download Cells that move organs and body parts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
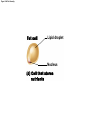
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Cell Extensions • Surface extensions found in some cells – Cilia move materials across the cell surface • Located in the respiratory system to move mucus – Flagella move the cell • The only flagellated cell in the human body is sperm – Microvilli are tiny, fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane • Increase surface area for absorption – Common in intestines and kidneys © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Cell Diversity • The human body houses over 200 different cell types – Don’t worry- you don’t have to know them all! • Cells vary in length from 1/12,000 of an inch to over 1 yard (nerve cells) • Cell shape reflects its specialized function – an example of how structure determines function © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Cell Diversity • Cells that connect body parts – Fibroblast • Secretes cable-like fibers – Erythrocyte (red blood cell) • Carries oxygen in the bloodstream © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.8a Cell diversity. Fibroblasts Rough ER and Golgi apparatus No organelles Nucleus Erythrocytes (a) Cells that connect body parts Cell Diversity • Cells that cover and line body organs – Epithelial cell • Packs together in sheets • Intermediate fibers resist tearing during rubbing or pulling © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.8b Cell diversity. Epithelial cells Nucleus Intermediate filaments (b) Cells that cover and line body organs Cell Diversity • Cells that move organs and body parts – Skeletal muscle and smooth muscle cells • Contractile filaments allow cells to shorten forcefully © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.8c Cell diversity. Skeletal muscle cell Contractile filaments Nuclei Smooth muscle cells (c) Cells that move organs and body parts Cell Diversity • Cell that stores nutrients – Fat cells • Lipid droplets stored in cytoplasm © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.8d Cell diversity. Fat cell Lipid droplet Nucleus (d) Cell that stores nutrients Cell Diversity • Cell that fights disease – Macrophage (a phagocytic cell) • Digests infectious microorganisms © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.8e Cell diversity. Lysosomes Macrophage Pseudopods (e) Cell that fights disease Cell Diversity • Cell that gathers information and controls body functions – Nerve cell (neuron) • Receives and transmits messages to other body structures © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.8f Cell diversity. Processes Rough ER Nerve cell Nucleus (f) Cell that gathers information and controls body functions Cell Diversity • Cells of reproduction – Oocyte (female) • Largest cell in the body • Divides to become an embryo upon fertilization – Sperm (male) • Built for swimming to the egg for fertilization • Flagellum acts as a motile whip © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 3.8g Cell diversity. Flagellum Nucleus Sperm (g) Cell of reproduction Cell Physiology • Cells have the ability to: – Metabolize – Digest food – Dispose of wastes – Reproduce – Grow – Move – Respond to a stimulus © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.