* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Cell
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
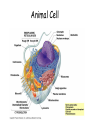
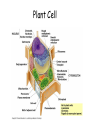
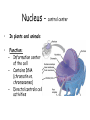
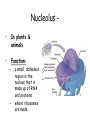
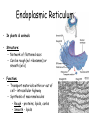
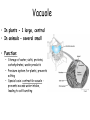
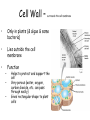
Animal Cell Plant Cell Cell Membrane – outer boundary – In plants & animals – Structure: – • Phospholipid bilayer • Contains lipids (bilayer), proteins (channels), and carbohydrate chains (identification cards) – hydrophilic heads, hydrophobic tails Function: • • • Regulates what enters and leaves the cell Semi-permeable membrane Protection and support Nucleus • In plants and animals • Function: – Information center of the cell – Contains DNA (chromatin vs. chromosomes) – Directs/controls cell activities control center Nucleolus • In plants & animals • Function: – – a small, darkened region in the nucleus that is made up of RNA and proteins where ribosomes are made Mitochondria • In plants & animals • Structure: – Double membrane • Cristae - inner folds, increase surface area • Outer membrane for protection of cell • Function: – “Powerhouse” of the cell – Able to self-replicate ( # in cells with high energy need) – Releases energy from food for the organism to use Ribosomes • In plants & animals • Structure: – Little “dots” – Small (25 nm) ball-like structures – Found free-floating in cytoplasm or attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum – Composed of RNA and protein • Function: – Synthesis of proteins (where proteins are made) Endoplasmic Reticulum • In plants & animals • Structure: – Network of flattened sacs – Can be rough (w/ ribosomes) or smooth (w/o) • Function: – Transport materials within or out of cell – intracellular highway – Synthesis of macromolecules • Rough - proteins, lipids, carbs • Smooth - lipids Lysosome • In animals only • Structure: – Small, circular structures – Found only in animal cells – Contain digestive enzymes • Function: – Digestion of: • Worn out organelles • Debris • Large ingested particles – Lysosomes are responsible for your hands not being webbed!! Golgi Apparatus • In plants & animals • Structure: – Flattened stacks of membranes – Vesicles attached to top and bottom • Function: – Collection, modification, packaging of proteins and other substances • Vesicles attach, deposit materials • GA modifies materials based on needs • Vesicles attach to membrane and distribute modified substances Vacuole • In plants - 1 large, central • In animals – several small • Function: – Storage of water, salts, proteins, carbohydrates, waste products – Pressure system for plants, prevents wilting – Special case: contractile vacuole prevents excess water intake, leading to cell-bursting Cell Wall – surrounds the cell membrane • Only in plants (& algae & some bacteria) • Lies outside the cell membrane • Function – – – Helps to protect and support the cell Very porous (water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, etc. can pass through easily) Gives rectangular shape to plant cells Plastids • Only in plants • Function: – Chloroplast - Conversion of light energy (sun) into chemical energy (glucose/food) – Chromoplasts – Store pigments (ex. carrot root cells, flower petals) – Amyloplasts - Store food/starch Cytoskeleton • In plants – microtubules, intermediate filaments, microfilaments • In animals – all • Function: maintains cell shape and provides internal support – Microtubules - hollow tubes of proteins, hold organelles in place, maintain shape, act as tracks that guide organelle movement – Intermediate filaments – rods that anchor organelles in place – Microfilaments – long & threadlike, used for cell movement – Cilia – short, hairlike projections used for cell movement – Flagella – long, taillike projections used for movement – Centrioles – organize microtubules during cell division framework Who Am I? (quick review) • I stated all plants are made of cells • I stated all cells come from the division of preexisting cells • I coined the term “cell” when I looked at slices of cork and dead plant cells • I am given credit for developing the 1st mini microscope and I looked at pond water and made detailed drawings • I discovered all animals are made of cells • List 3 organelles you learned about today. • Describe the function of each of the organelles you listed. • Yes, you should write your name on the paper