* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells Types
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
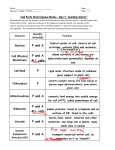
Cell Structure & Function Agenda: Observe short presentation. Partner check handout… Trade with person next to you. Sign “Graded By…” on bottom. Review Cell theory 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure & function in all living things 3. All cells come from preexisting cells Cells Types Prokaryote Organisms that have DNA not bound in a nucleus Bacteria Very Small Very Old (3.5 BYO) Simple Eukaryote Organisms with DNA in a nucleus Animals Plants Protists Fungus 10-100x larger Younger in evolution (1.5 BYO) Complex cellular organization with many organelle Cell Structure & Function There are 4 basic structures of all cells: A. Cell membrane The vocab B. Nucleus term for all of the structures found C. Cytoplasm in the cell is: D. Ribosomes ORGANELLES Ribosomes Cytoplasm Animal Cell DNA Cell Membrane Plant 1. Cytoskeleton/Cytoplasm The fluid interior of the cell. This is where all the organelle float around. Contains: 2. Microtubules 3. Microfilaments 4. Intermediate fibers 1. Cytoskeleton A variety of filaments and fibers that support cell structure and drive cell movement. 5. Nucleus 8. DNA/ Chromosomes 7.Nucleolus 6. Nuclear Envelope The control & information center of the cell, houses DNA. 6. Nuclear Envelope *membranes that surround the nucleus *contains pores which allow movement of materials in & out of nucleus 7. Nucleolus -small region that contains RNA and proteins. -Ribosomes are made here. 8. DNA Contain the genetic information that must be passed to each new generation of cells. 9. Ribosomes Protein Factories Two Types: 10. Free 11. Bound 12. Lysosome - Filled with enzymes necessary for digesting waste materials in the cell. - The cells “cleanup crew” - Vesicles help move stuff around the cell. 14. Rough ER 13.Endoplasmic Reticulum Modifies and ship proteins 15. Smooth ER What do you notice to be the difference? Ribosomes on rough ER 14. Rough ER Has ribosomes attached to the surface. Makes & modifies proteins that are meant to leave the cell. 15. Smooth ER Does not have ribosomes attached to the surface. Modifies and breaks down lipids & toxins. 16. Golgi Apparatus The apparatus packages proteins & substances for storage in the cell or to be released from the cell Outer Membrane 17.Mitochondria Inner Membrane Cristae Matrix The “powerhouse” of the cell. Converts the chemical energy stored in food into usable compounds for the cell. 18. Plasma Membrane Glycoproteins Embedded Proteins Regulates what enters and leaves the cell. It also aids in the protection and support of the cell. Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Bilayer Lipids line up based on hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Embedded Proteins Proteins help to move molecules across the membrane using both passive and active transport. Glycoproteins Used for cellular recognition and binding sites. E.C. Centriole What is my job? 20. Vacuole Saclike structures that store materials such as water, salts, proteins, & carbohydrates. Chloroplast Vacuole Plant Cell Cell Wall 19. Chloroplast Contain chlorophyll that trap the energy of sunlight & convert it into chemical energy 20. Vacuole RECALL - saclike structures that store materials such as water, salts, proteins, & carbohydrates. IN PLANTS – There is a single large central vacuole filled with liquid that causes pressure making it possible for plants to grow quickly & support heavy structures like leaves and flowers 21. Cell Wall Strong, non-living structure made of cellulose that surrounds plants, algae and some bacteria. Provides protection and support for the plant cells. It is very porous so that water, oxygen, carbon dioxide and other substances can pass through easily. BACTERIAL CELL. PROKARYOTE 22. Plasmid • Extra DNA the can be traded with other neighboring bacteria. • Contains information like antibiotic resistance. 23. Pili • A tube of proteins that allow bacteria to trade plasmids. • Docking mechanism for bacteria. • Not only found in bacteria, flagellum allow cells to perform locomotion. 24. Flagellum 25. Peptidoglycan Capsule • A variable substance on the outside of some bacteria that allows it to form dense colonies. • Kinda like slime. 1. 2. 3. Cell membrane Cytoplasm DNA 100% 0% 1 0% 2 3 Cytoskeleton A B C D What is labeled here? Click to animate the image. 1. 2. 3. 4. Ribosome Smooth ER Rough ER Nucleus 100% 0% 1 0% 2 3 0% 4 1. 2. 3. 4. Ribosomes Mitochondria Lysosomes Golgi apparatus 94% 0% 1 6% 2 0% 3 4 1. 2. 3. 4. Cell wall Nucleus Capsule Lysosome 25% 1 25% 25% 2 3 25% 4 Which cellular component is common to BOTH eukaryotes and prokaryotes? Cell wall Nucleus Capsule Lysosome Which cellular component is common to BOTH eukaryotes and prokaryotes? Cell wall (don’t forget plant cells! Plant AND bacteria cells) Nucleus (eukaryotes ONLY) Capsule (prokaryotes ONLY) Lysosome (Eukaryotes ONLY) B Click to animate the image. C D A E F http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model .htm What is the order? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The ER membrane pinches off to encircle the protein. The vesicle with the protein enters one end of the Golgi apparatus. In the nucleus, DNA instructions are copied as RNA messages. Proteins cross the membrane of the rough ER and enter the ER. The finished protein leaves the other end of the Golgi apparatus in a new vesicle that buds from the organelle’s surface. 6. The finished protein travels through the cytoplasm to the cell membrane. 7. The vesicle fuses with the cell membrane, releasing the protein out of the cell. 8. The vesicle holding the protein travels through the endoplasmic reticulum and out into the cytoplasm. 9. RNA messages travel to bound ribosomes, where proteins are made. 10. The protein is modified by enzymes. 11. The finished protein is repackaged, enclosed in a new vesicle.