* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download notes
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
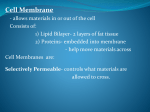
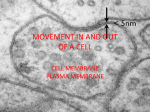
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
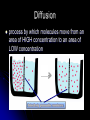
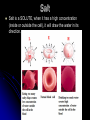
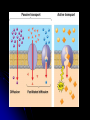
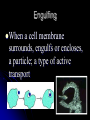
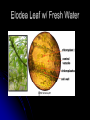
Cell Transport Osmosis and Diffusion NOTES Page 80-85 The cell membrane is selectively permeable Only some substances can pass through the membrane while others cannot What are some things that have to pass the cell membrane? Cells need oxygen and food to enter the cell and waste products must leave the cell. Diffusion process by which molecules move from an area of HIGH concentration to an area of LOW concentration What Causes Diffusion? Molecules are always on the move They bump into each other As the bump they begin to spread out What do you think the goal of diffusion is? Goal is to get to equilibrium : Equal concentration on either side of the membrane Osmosis The diffusion of WATER through a selectively permeable membrane Cells depend on water for many functions, so osmosis is a very important process. Salt Salt is a SOLUTE, when it has a high concentration (inside or outside the cell), it will draw the water in its direction. Passive vs. Active Transport Passive transport: movement of materials across the membrane without using energy Goes with the concentration gradient HIGH TO LOW Active transport: movement of materials across the membrane using energy Goes against the concentration gradient LOW TO HIGH Active Transport Sometimes proteins in the cell membrane need to help move substances into the cell Active transport: can pedaling up hill, need a lot of energy. Engulfing When a cell membrane surrounds, engulfs or encloses, a particle; a type of active transport Why are cells SO small? As a cell’s size increases, more of its cytoplasm is located farther from a cell membrane Takes too long to get materials entering the cell to their destination Takes too long to remove wastes from inside the cell With you lab group, discuss how osmosis, diffusion, and active transport are connected to homeostasis Elodea Leaf w/ Fresh Water Elodea Leaf w/ Salt Solution Label the parts: A. Cell Wall B Chloroplast