* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Look at Mitosis in Action!
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
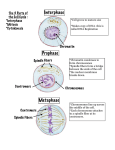
Mitosis in Action Let’s Explore the Stages of Mitosis What is Mitosis? • Mitosis is cell division where the replicated (cloned) genetic material in a parent cell is equally distributed to two daughter cells. What is Mitosis? • Mitosis allows organisms to grow, increase their size by adding more cells & • Replace damaged cells. The Stages of Mitosis • Interphase (not a true phase of mitosis) • prophase • metaphase • anaphase • telophase Interphase • • • • The phase between cell divisions There is still a lot going on. The cell puts on mass. The DNA makes a “photocopy” of itself. Therefore, the # of chromosomes has doubled in number. They are in the form of thin, stringy CHROMATIN! Spindle fibers will extend from the centromeres in later stages. Chromatin is a long stringy form for DNA found in the Interphase Stage Prophase • 1st TRUE step in mitosis. • The stringy chromatin condenses into individual chromosomes. Each chromosome contains 2 chromatids joined at a centromere. • The nuclear membrane breaks down. • Spindles form at opposite ends of the cell. Anatomy of Chromosomes Kinetochores are fibers that will attach to the spindles. The coiled chromatin become the two chromosomes (2 pairs of chromatids) attached at the centromere. Metaphase • The spindle fibers extend from the poles of the cell to the center line. • The chromosomes line up at the center line of the cell. • Spindle fibers attach to the kinetochores at the centromeres on each side of the chromatids. Anaphase • The paired chromatids begin to separate and move toward the poles. • Each of the separated pairs of chromatids are a full chromosome. • The poles of the cell stretch further apart to make the cell longer. Telophase • Nuclear membranes begin to form around the chromosomes at the opposite poles of the cell. • The chromosomes uncoil to become stringy chromatin fibers again (the normal form of DNA) Cytokinesis • The cytoplasm and organelles separate into two equal portions. • The plasma membrane pinches in to form two separate, new daughter cells. Try to identify the stages: Which stage is this? Which stage is this? Which stage is this? Which stage is this? Which stage is this? Which stage is this? Which stage is this? Which stage is this? Which stage is this? Which stage is this? Which stage is this?