* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
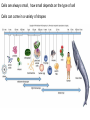
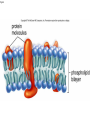
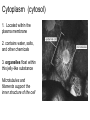
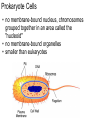
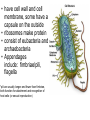
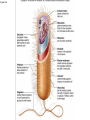
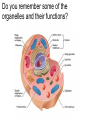
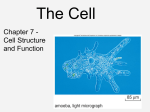
The Cell Cell Structure and Function Early Contributions • Robert Hooke - First person to see cells, he was looking at cork and noted that he saw "a great many boxes. (1665) • Anton van Leeuwenhoek - Observed living cells in pond water, which he called "animalcules" (1673) • Theodore Schwann - zoologist who observed tissues of animals had cells (1839) • Mattias Schleiden - botanist, observed tissues of plants contained cells (1845) • Rudolf Virchow - also reported that every living thing is made of up vital units, known as cells. He predicted that cells come from other cells. (1850 ) The Cell Theory • 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. • 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest unit that can perform life functions. • 3. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. *Why is the Cell Theory called a Theory and not a Fact? Cells are always small, how small depends on the type of cell Cells can come in a variety of shapes Figure 4.3 Single Cheek Cell - at different illuminations Three Features of Cells 1. Plasma (Cell) Membrane - serves as a barrier, regulates what enters and leaves the cell * We go into much more detail in the next chapter on how this works* Cell Membrane is made of: a) Phospholipid Bilayer (double layer) b) Proteins c) Carbohydrates Pg 64 2. Genetic Material 1. provides cellular "blueprint" that controls the functions of the cell 2. In the form of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) 3. DNA is universal for all cells, an all living things - evidence of common ancestry 4. Chromatin is the complex of proteins and DNA, it condenses into chromosomes before cell division *We will go into much greater detail in a later unit on GENETICS* Cytoplasm (cytosol) 1. Located within the plasma membrane 2. contains water, salts, and other chemicals 3. organelles float within this jelly-like substance Microtubules and filaments support the inner structure of the cell Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Cells Endosymbiosis theory: All organelles seem to share many properties with bacteria. Lynn Margulis proposed endosymbiont hypothesis (endosymbiosis): that organelles derived from ancient colonization of large bacteria (became the eukaryotic cell) by smaller bacteria (became the mitochondria, chloroplast, etc.) Symbiosis = "living together". *Mitochondria & Chloroplasts have their own DNA Animation at Microbiological Concepts Prokaryote Cells • no membrane-bound nucleus, chromosomes grouped together in an area called the "nucleoid" • no membrane-bound organelles • smaller than eukaryotes • have cell wall and cell membrane, some have a capsule on the outside • ribosomes make protein • consist of eubacteria and archaebacteria • Appendages include: fimbriae/pili, flagella *pili are usually longer and fewer than fimbriae, both function for attachment and recognition of host cells (or sexual reproduction) Figure 4.4a E. coli Eukaryote Cells • • • • has a membrane-bound nucleus has membrane-bound organelles in cytoplasm organelles perform specific functions much larger than prokaryotes Organisms within the animal, protist, plant and fungi kingdoms are all eukaryotes Do you remember some of the organelles and their functions? Quick Recap....... 1. What are the two main types of cells? 2. Which one is larger? 3. Which one does not have a membrane-bound nucleus? 4. What are the three main parts of the cell (that all cells have)? 5. What are the 3 components of the cell theory? 6. What theory explains how eukaryotes evolved? It may seem that in these slides there were quite a few "more on this later.." notes.... That's because cell biology is a huge area, and is divided into many branches that biologists specialize in... 1) Oncology 2) Microbiology 3) Genetics 4) Paleobiology 5) Pathology ............to name a few Here's an older video that compares prokaryotes and eukaryotes and discusses how cells evolved, film by the Phoenix Learning Group (17 minutes) And a shorter video on the main parts of The Cell