* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitosis
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
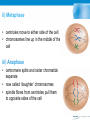
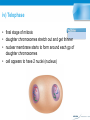
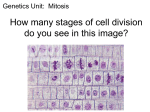
THE CELL CYCLE • 2.5 As eukaryotic cells grow and divide, they move through three distinct stages: 1. interphase – cells grow and prepare to divide 2. mitosis – cells start to divide 3. cytokinesis – two cells are formed from one 1. Interphase: • the cell carries out all normal life activities • the DNA is in very long, thin, and invisible strands • DNA is copied at end of interphase to get ready for division • most of the cell’s life is spent in interphase HowStuffWorks Videos "Interphase: The Resting Stage" 2. Mitosis • the DNA doubles, to get ready to be divided • there are 4 phases of mitosis i) Prophase: • DNA thickens • 2 identical strands of DNA (copied during interphase) called chromosomes • chromosome made of 2 identical sister chromatids • each chromatid held together by a centromere • nuclear membrane disappears • YouTube - Mitosis: The Phases, Part 1 of 2, from Thinkwell Biology PHASES OF CELL DIVISION 2.5 ii) Metaphase • centrioles move to either side of the cell • chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell iii) Anaphase • centromere splits and sister chromatids separate • now called ‘daughter’ chromosomes • spindle fibres from centrioles pull them to opposite sides of the cell iv) Telophase • final stage of mitosis • daughter chromosomes stretch out and get thinner • nuclear membrane starts to form around each gp of daughter chromosomes • cell appears to have 2 nuclei (nucleus) Cytokinesis • • • • cell’s cytoplasm divides cell membrane pinches off splits into 2 new daughter cells each cell is identical to the original parent cell YouTube - Mitosis: The Phases, Part 2 of 2 from Thinkwell Biology