* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transport Chapter 5 - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
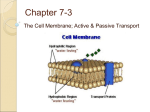
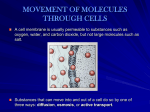
Transport Chapter 5 How does stuff get in and out of a cell through the cell membrane? How do molecules move? All molecules will move automatically from a region of ______ HIGH concentration to a region of ______concentration. LOW DIFFUSION _______________ DIFFUSION Molecules will keep moving until the concentration is EQUAL everywhere = __________________________ EQUILIBRIUM What if the HIGH and LOW places are on different sides of a cell membrane? Molecules will still go from HIGH to LOW if the cell membrane will let them through! Some molecules can just pass right through the bilayer using DIFFUSION oxygen, carbon dioxide EXAMPLE: ___________________ OSMOSIS • When water molecules move across membrane from HIGH to LOW it is called OSMOSIS ___________________ Cell Membrane Controls what enters & leaves the cell Only certain kinds of molecules can go across SELECTIVELY = ______________ PERMEABLE (Semi-permeable) PROBLEM WITH CELLS What if a cell needs a molecule that can’t pass through the cell membrane easily? Not all molecules can pass through easily Need a way to move molecules across that can’t go by DIFFUSION Carrier Proteins ___________________________ INTEGRAL PROTEINS that help molecules go across Vesicles ___________________________ Small membrane sacs that carry molecules 2 KINDS of TRANSPORT • ______________ PASSIVE TRANSPORT Does NOT require energy ACTIVE • _____________ TRANSPORT Requires energy CARRIER PROTEINS PERIPHERAL INTEGRAL VESICLES CARRIER PROTEINS FACILITATED DIFFUSION FACILITATED DIFFUSION PASSIVE (No energy needed) HIGHER TO LOWER CARRIER PROTEINS GRAB & FLIP IT ACROSS GLUCOSE EXAMPLE: _________________ ION CHANNEL ION CHANNELS • PASSIVE (No energy needed) • HIGHER TO LOWER • CARRIER PROTEINS MAKE A PASSAGEWAY • Examples in cells: _______________________ Na+ , Cl- , Ca + + , K + PROBLEM WITH CELLS What if cell needs to move from LOW to HIGH? What if cell needs to move it fast and not wait? ENERGY IF YOU NEED TO ADD __________ WANT A MOLECULE TO MOVE IN THE OPPOSITE DIRECTION IT NATURALLY GOES! What organelle supplies the energy? + Na and K + PUMP SODIUM-POTASSIUM PUMP • ACTIVE (Uses energy) • USES CARRIER PROTEIN • Special just for Na+ and K + ions • Examples in cells: 3 Na+ are pumped out of cells at same time 2 K + are taken into cells VESICLES ENDOCYTOSIS Brings substances into cell • ACTIVE • VESICLES CARRY MOLECULES INTO CELL – Fluid, molecules = Pinocytosis – large particles or whole cells = Phagocytosis • Examples in cells: – one celled organisms eat this way – white blood cells destroy bacteria this way Endocytosis EXOCYTOSIS Substances are released outside of cell • ACTIVE • VESICLES CARRY & RELEASE MOLECULES • Examples in cells: –GOLGI BODIES release packaged proteins Exocytosis INSIDE CELL OUTSIDE CELL Endocytosis & Exocytosis http://grossmont.gcccd.cc.ca.us/cmilgrim/Bio120/Outline/ Outline2.gif/TransportMedia/EndoExocytosisMovie.htm PASSIVE TRANSPORT • Diffusion • Osmosis • Facilitated Diffusion • Ion Channels DIFFUSION WITHOUT a membrane • • • • • PASSIVE HIGH TO LOW NO CARRIER PROTEINS NO VESICLES ANY MOLECULES BUT WATER DIFFUSION ACROSS a membrane • • • • • PASSIVE HIGH TO LOW NO CARRIER PROTEINS NO VESICLES ANY MOLECULES BUT WATER OSMOSIS • • • • • PASSIVE HIGH TO LOW NO CARRIER PROTEINS NO VESICLES FOR WATER MOLECULES FACILITATED DIFFUSION • PASSIVE • HIGH TO LOW • USES CARRIER PROTEINS ION CHANNELS • • • • • PASSIVE HIGH TO LOW NO VESICLES USES CARRIER PROTEINS FOR IONS ACTIVE TRANSPORT •Na+-K+ Pump •Exocytosis •Endocytosis Pinocytosis Phagocytosis SODIUM-POTASSIUM PUMP • ACTIVE • USES CARRIER PROTEIN • Special just for Na+ and K + ions EXOCYTOSIS & ENDOCYTOSIS • ACTIVE (Need energy) • USES VESICLES PASSIVE TRANSPORT • • • • Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Ion Channels ACTIVE TRANSPORT •Na+-K+ Pump •Exocytosis •Endocytosis Pinocytosis Phagocytosis THE END OSMOSIS OSMOSIS ISOTONIC: EQUALS Concentration outside cell ____________ concentration inside cell Water entering = water leaving STAYS THE SAME SIZE so cell _____________________ OSMOSIS HYPERTONIC: Concentration outside cell is ____________________ GREATER THAN inside cell More water leaves cell than enters so cell shrinks ______________________ = PLASMOLYSIS OSMOSIS HYPOTONIC: Concentration outside cell is ________________ LESS THAN inside the cell More water enters than leaves cell so cell expands and can burst ___________________ = CYTOLYSIS Animal cells Plant cells IS IT ISO, HYPO, HYPER? Named for LIQUID concentration NOT cell concentration More solute OUTSIDE than inside cell Cell will shrink (PLASMOLYSIS) HYPERTONIC LESS solute OUTSIDE than inside cell Cell will swell & burst (CYTOLYSIS) HYPOTONIC EQUAL inside and outside Cell stays the same size ISOTONIC Really THE END