* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2-Inside-a-cell
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
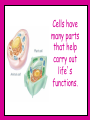
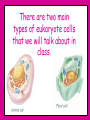
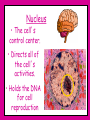
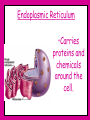
Inside Cells! What do you see when you look at yourself in the mirror? Skin, hair, eyes, teeth, muscles? Let’s get a closer look…. Under a microscope, (on low power), your skin looks like this: But upon even closer look… And closer still.. …and that’s just your skin! ALL of you is made up of all different kinds of cells. muscle cells heart cells brain cells Under a microscope, you can see these cells. Everything that is alive is made of cells. Cells were named by the English scientist Robert Hooke (1635-1703) Hooke discovered the empty spaces and “walls” when looking at cork under a microscope. These reminded him of monks “cells” and the name stuck! Other Scientists the contributed to cell knowledge: Schleiden – discovered that plants were made up of cells. Schwann – discovered that animals were made up of cells. Virchow – stated that all living things come from other living things. All contributed to the Cell Theory! THE CELL THEORY 1.All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of all living things. 3. Cells can only be produced by other living cells. There are 2 main types of cells: Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic (no true nucleus) (has a nucleus) Living things made out of just one cell are called SINGLE-CELLED ORGANISMS Living things made of more than one cell are called MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS So what the heck is a cell? If you remember… Atoms and molecules make up all matter. Cells are MUCH larger, and they make up all of life. To understand how living things work, you have to know about cells. Cells allow us to breathe, grow, get energy from our food, and even see! Cells have many parts that help carry out life’s functions. There are two main types of eukaryote cells that we will talk about in class. Let’s start with the animal cell… Cell Membrane The outer covering of an animal cell. Cell Membrane • Gives support to the cell. It holds everything in! 2. Allows food to come in and waste to go out through openings called PORES Nucleus The large round(ish) mass in the cell. Has a membrane around outside. Nucleus • The cell’s control center. • Directs all of the cell’s activities. • Holds the DNA for cell reproduction DNA is what causes you to have the color hair, eyes, and height that you have! (and a lot of other things too) Cytoplasm The “empty” space inside the cell. Made of a thick, jellolike substance. All of the ORGANELLES (tiny cell structures) float around in the cytoplasm. Mitochondria The small organelles with an inner folded membrane. Mitochondria The “Powerhouses” of the cell. Mitochondria •They digest sugar molecules and provide energy for the cell. •Then they give off carbon dioxide as waste. Ribosomes Small, grainlike bodies floating in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes produce proteins…they are like little protein factories Endoplasmic Reticulum A maze of passageways in the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum •Carries proteins and chemicals around the cell. Golgi Bodies A structure of flattened sacs and tubes. Golgi Bodies •Receives proteins from the ER and SORTS and DISTRIBUTES them to all parts of the cell Vacuoles •Storage organelles. ? •Both nutrients and waste can be stored here. Lysosomes •The cell’s digesters. They digest old cell parts and recycle the usable materials. Now for the plant cell… They have everything mentioned and 2 more… Chloroplasts Able to convert sunlight into food (sugar). This is where photosynthesis takes place Cell Wall Rigid support surrounding the cell membrane to keep the cell stiff and firm.