* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
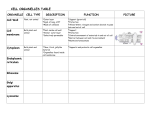
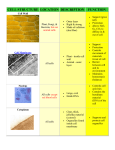
Cell Organelles Their Structures and Functions Prokaryotic Bacteria Cell Eukaryotic Plant Cell Eukaryotic Animal Cell Body Cell Cell (Plasma) Membrane • Structure - The lipid bilayer that forms the outer boundary of a cell • Function(s) - Regulates movement of molecules into and out of cells; semipermeable • Found In - Bacteria, Animal & Plant Cells Cytosol (Cytoplasm – the cytosol and all the organelles within the cell) • Structure - Gelatinous aqueous fluid that fills the cell • Function(s) - Suspends the organelles within the cell - Fills the cell and gives it shape - Allows nutrients to move about the cell • Found In - Bacteria, Animal & Plant Cells Nucleus • Structure - The most prominent organelle, surrounded by a double membrane perforated with pores • Function(s) - Regulates all cell activities - Contains the DNA of the cell • Found In - Animal and Plant Cells Nucleolus • Structure - Small circular structure(s) within nucleus • Function(s) Synthesis and partial assembly of ribosomes • Found In - Animal and Plant Cells Nuclear Envelope • Structure - Double membrane with pores surrounding the nucleus • Function(s) - Regulates movement of molecules into and out of the nucleus • Found In - Animal and Plant Cells Chromatin (DNA) • Structure - Fine strands of genetic information (DNA and protein); coils to form chromosomes • Function(s) - Contains the code that directs most cell activities - DNA’s code is the instructions for making proteins • Found In - Bacteria, Animal & Plant Cells Mitochondria • Structure - A peanutshaped organelle which has a double membrane. The inner membrane has many folds. • Function(s) – Performs cellular respiration; generates ATP (the energy the cell needs to run) • Found In - Animal and Plant Cells Ribosomes • Structure - Dot-like organelles attached to the rough ER or free in the cytosol • Function(s) – Reads RNA to synthesize proteins • Found In - Bacteria, Animal & Plant Cells Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Structure – a system of membranous tubes and sacs covered with dark dots (ribosomes) • Function(s) - Makes alterations to proteins produced by ribosomes - Folds proteins into the correct shapes • Found In - Animal and Plant Cells Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum • Structure - A system of membranous tubules and sacs • Function(s) - helps move lipids, steroids, and fatty acids within the cell (intracellular highway); regulates calcium levels; breaks down toxic substances • Found In - Animal and Plant Cells Golgi Apparatus (Complex) • Structure - A series of flattened sacs with a characteristic convex shape • Function(s) – Processes and packages proteins and substances produced by cells; instructs the substances where to go • Found In - Animal and Plant Cells Lysosomes • Structure - Small spherical organelles that enclose digesting enzymes within single membranes • Function(s) - Digests molecules, old organelles, and foreign substances; recycling center • Found In - Animal and Plant Cells Digesting enzymes Cytoskeleton (microtubules and microfilaments ) • Structure - A network of long protein strands located in the cytosol • Function(s) - Provides internal shape and support to cells (microfilaments and microtubules) • Found In - Animal and Plant Cells Flagella and Cilia • Found In - Bacteria and Animal Cells • Structure - Flagella: Whip-like tail(s) extending from the surface of some cells - Cilia: Short hair-like organelles that extend from the surface of some cells • Function(s) - Propel the cell through the environment - Move materials over the surface of the cell Centrioles • Structure - Cylindrical bodies that appear during cell division • Function(s) – Help move DNA during division in animal cells • Found In - Animal cells only Cell Wall • Structure - A rigid covering that lies outside the cell membrane made of long chains of cellulose • Function(s) - Provides external protection and support to plant cells • Found In – Plants cells only (Bacteria can have a cell wall but it is biochemically different from plant cell walls) Vacuole • Structure - Fluid filled membranous sac • Function(s) - Stores enzymes and wastes; cell’s warehouse • Found In - Animal and Plant Cells (Can be very large in plants cells, but small in animal cells) Plastid • Structure - Organelles surrounded by two membranes and contain their own DNA • Function(s) - Stores food or pigment • Found In - Plant cells only Chloroplast • Structure - Oval organelle surrounded by a double membrane that encloses a system of flattened membranous sacs • Function(s) – Contains chlorophyll and performs photosynthesis; a type of plastid. • Found In - Plant cells only