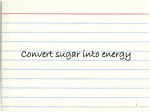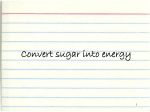* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell membrane – boundary that separates the interior of
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane – boundary that separates the interior of the cell from its surroundings; phospholipid bilayer, semi-permeable Cytoplasm – the cytosol (gel like substance) and organelles; cytosol: 70% of the cell volume, made of water, salts, and organic molecules Nuclear membrane – a pair of membranes that surrounds the nucleus (DNA), contains pores Nucleolus – ball-like mass of fibers, contains the parts that make up ribosomes Golgi apparatus – modifies, stores, and routes proteins and other chemicals Rough endoplasmic reticulum – ER that contains ribosomes – network of membranes that makes and transports proteins Smooth endoplasmic reticulum – ER that doesn’t contain ribosomes, builds lipid molecules like hormones Ribosome – organelles that work as protein “assembly lines,” clusters of proteins and nucleic acids that reads RNA and joins amino acids Mitochondria – site of cellular respiration, releases energy from sugar and uses it to form ATP Peroxisome – breaks down fatty acids, contains hydrogen peroxide that is later changed to water by catalase Centriole – involved in the organization of mitotic spindles and in the completion of cytokinesis (cell division) Lysosome – membrane-bound sacs that contain digestive enzymes to break down proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides; recycling center; destroys bacteria Cytoskeleton – network of fibers that runs throughout cytoplasm and gives cell shape and stability; fibers are microtubules and microfilaments Vacuole – stores undigested nutrients, isolates materials that may be harmful to the cell Chloroplast – site of photosynthesis (conversion of light energy into chemical energy – glucose) Cell wall – rigid layer of polysaccharides outside cell membrane composed mainly of cellulose (fiber) Large central vacuole – stores chemicals like salts, absorbs water, may contain pigments or poisons