* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
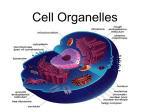
Cells Discovery of Cells 1665: Robert Hooke looking at cork under crude microscope In 1673, van Leeuwenhoek saw unicellular organisms in pond scum First to see bacteria and yeast Two centuries pass; Schleiden (1838) proposes all plants are made of cells Schwann makes same claim for animals Wrote first Cell Theory: 1. 2. All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cell is basic unit of life. All plants are made of cells! Wow! So are all animals! Let’s make up a “cell theory”! Who wrote the first two parts of the cell theory? A. B. C. D. E. Hooke van Leeuwenhoek Schleiden Schwann Both C and D 20 years later, Virchow saw that all cells come from other cells Added 3rd part of cell theory: 3. All cells come from existing cells. All cells come from other cells!! All cells have… Lots of different kinds of cells, but all have: Cell Membrane DNA Cytoplasm Organelles Small Size Which of the following is NOT something that ALL cells have in common? A. B. C. D. E. F. Cell Membrane DNA Chloroplasts Cytoplasm Organelles Small Size Cell Membrane Also called plasma membrane Surrounds all cells Has holes to allow things in and out Which of the following is NOT true of the cell membrane? a. b. c. d. Also called plasma membrane Surrounds all cells Only found in animal cells Has holes to allow things in and out DNA Hereditary material Controls all of the cell’s activities Has info needed to make new cells Which of the following is NOT true of DNA? a. b. c. d. It is the hereditary material It makes fats for the cell It controls all of the cell’s activities It has the info needed to make new cells Cytoplasm Fluid that fills the cell Organelles Structures inside that perform special jobs for the cell (example: ribosomes=make protein, etc.) Small Size Almost all require use of microscope Large organisms have more cells, not bigger ones!! Two types of Cells Prokaryotic Bacteria! No nucleus Organelles are not covered with a membrane DNA is a circle Eukaryotic All other cells Has a nucleus Organelles are covered with a membrane (skin) DNA is linear (in a line) Identify which cell is prokaryotic. A B Eukaryotic Cells Very complex! Inside parts (organelles) are difficult to see Cell Membrane Double layer Has pores (holes) which allow things in and out Selectively permeable = “choosy” about what enters and leaves the cell. Cell Wall Plants, algae and fungi only Made of cellulose Strength and support Which of the following is NOT true of cell walls? A. Plant cells and fungi cells have them. B. Animal cells have them. C. They are made of cellulose. D. They provide strength and support for the cell. Nucleus Nucleus means “kernel” or “nut” Membrane covered, with holes so things can pass through Control center: stores DNA (instructions for making protein and reproduction) Ribosomes Cells are made of proteins. Amino acids link together to make proteins at ribosomes = Protein Endoplasmic reticulum Also called ER Makes lipids (fats) Breaks down drugs and other dangerous chemicals Also delivery system of cell Rough and Smooth Which of the following is not true of endoplasmic reticulum? A. Also called ER B. Makes lipids (fats) C. Breaks down drugs and other dangerous chemicals D. Delivery system of cell E. Comes in only one type: rough ER Mitochondria Cells need energy. Where do they get it? Food is broken down for energy at the mitochondria Needs oxygen to function ATP ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE Chloroplasts In plants and algae Organelle which converts light energy, water, and carbon dioxide into sugar (FOOD!) Contain chlorophyll, the pigment that does this Golgi Complex Packages and ships materials out of the cell Looks like ER, but closer to cell membrane Little pieces can pinch off and leave the cell Lysosomes Filled with enzymes (chemicals which sometimes break things down) Destroy waste and old cell parts, as well as invaders Storage Centers Vesicles: membrane covered “bubbles” that form when part of the cell membrane surrounds something and pinches off Vacuoles: huge storage areas for water and other liquids, especially in plants The Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is similar to the skeletons in animals. They provide strength and structure. They help hold organelles in place. They can also help move things around inside a cell. Answer the following questions. Restart the PowerPoint to find them. DON’T GUESS! (True or False) Elephants have bigger cells than mice do. ___________ (True or False) To be selectively permeable means that you are not “choosy” about what materials you allow to enter and leave the cell. ___________ (True or False) Lysosomes digest waste and invaders through the use of enzymes (special chemicals). __________ (True or False) Oxygen is not needed when energy is made at the mitochondria. ______ (True or False) Amino acids are chemicals which link together to make carbohydrates. _______ (True or False) Proteins are assembled at ribosomes. __________ (True or False) There are three main types of cells: prokaryotic, eukaryotic, and protokaryotic. ________ (True or False) The Golgi Complex is similar to a post office; it packages materials for shipment out of the cell. ___________ Which of the following is NOT true of chloroplasts? A. B. C. D. Found in plants and algae. Changes sunlight and water into food. Found in some animal cells Contain the pigment chlorophyll. Which of the following is not true of the nucleus? A. Its name means “kernel” or “nut”. B. It has holes in it. C. It is only found in plant cells. D. It is the control center of the cell, containing the DNA.