* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
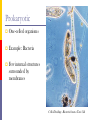
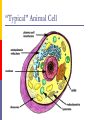
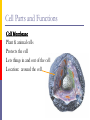
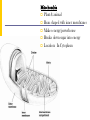
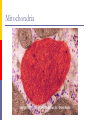
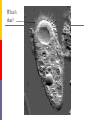
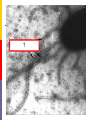
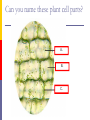
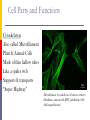
The Cell Structures & Functions AG BIO - McKee What is “Cell Theory”? The idea that all living things are made up of cells. What’s so special about cells? Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. Yeast Cells Where do cells come from? All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. Bean Cells in Mitosis Definition of the Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Would you like to see some examples? Even if you don’t, too bad. Remember… These are magnified images taken with microscopes Some cells have been stained with color so you can see them better. Nerve Cell Bacteria Cell Tree cells from the stomach of a possum. Brain Cell Cornstalk Cells Mammalian Tissue •Smooth muscle are structurally the simplest muscle cells •Provide contractile forces for most internal organs •Controls flow of blood through vessels and moves food through digestive tract. Two Types of Cells Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Prokaryotic One-celled organisms Example: Bacteria Few internal structures surrounded by membranes Cells Dividing: Bacteria from a Taxi Cab Eukaryotic Contain organelles surrounded by membranes Most living organisms Plant Humans & Animals “Typical” Animal Cell “Typical” Plant Cell Cell Parts and Functions Cell Wall Plant, not animal cells Outer layer, rigid, strong, stiff Made of cellulose Cell Parts and Functions Cell Membrane Plant & animal cells Protects the cell Lets things in and out of the cell Location: around the cell Cell Parts and Functions Nucleus Plant & animal cells Large & oval Control center Location: Inside the cell, Near the center Cell Parts and Functions Nucleolus (Nucleoli) Plant & animal cells Makes ribosomes Location: inside the nucleus (dark spot) Nuclear Membrane Plant & animal cells Protects around nucleus Lets things in/out of nucleus (pores) Selectively permeable cell Cell Parts and Functions Cytoplasm Plant & Animal Clear, thick, jellylike Holds all organelles in cell Location: in cell Cell Parts and Functions Chromatin/Chromosomes In Plant & Animal Cells Contains genetic information/traits Location: In nucleus Cell Parts and Functions Endoplasmic Reticulum (E.R.) Plant & animal cells Network of tubes and membranes Transports materials and sends messages to all parts of the cell Two types: smooth and rough (has ribosomes) Location: attaches from cell membrane to nuclear membrane Rough E.R. Cell Parts and Functions Ribosome Plant & Animal Cells Makes proteins Small circular shape Location: In Cytoplasm or Attached to E.R. Mitochondria Plant & animal Bean shaped with inner membranes Makes energy/powerhouse Breaks down sugar into energy Location: In Cytoplasm Mitochondria Cell Structure & Function Vacuole Plant = few/large Animal = small Fluid filled sacs Stores food, water & waste Location: In cytoplasm Vacuole What does a vacuole remind you of? Golgi Bodies or Golgi Apparatus Located in Plant & Animal Cells Packages and secretes Gets rid of waste Location: in cytoplasm What does a Golgi Body remind you of? GOLGI APPARATUS Cell Parts and Functions Lysosome Plant & Animal Cells Contains digestive enzymes Destroys bacteria, old cell parts… Location: in cytoplasm Centrioles Plant & Animal Cells Helps the cell to divide Location: in cytoplasm Cell Parts and Functions Cilia Most Plant, Animal & Bacteria Cells Short hair-like projections Used for movement Location: outside of cell Flagella Most Plant, Animal & Bacteria Cells Long whip-like tail Used for movement Location: outside of cell What’s that? ? Cell Structures and Functions Chloroplast Only in plant cells Contains chlorophyll Makes plants green Traps light energy from the sun Light Energy = Chemical Energy (Where photosynthesis occurs) Chemical Energy = Food for the Plant Cell Structures and Functions Plastids Found in Plant Cells Stores extra food Located in cytoplasm Can you name these plant cell parts? A. B. C. Cell Parts and Functions Cytoskeleton Also called Microfilament Plant & Animal Cells Made of thin hallow tubes Like a spider web Supports & transports “Super Highway” Microfilament (cytoskeleton) of mouse embryo fibroblasts, stained with FITC-phalloidin (100fold magnification.) Can you name these animal cell parts? Cell #1 Membrane #2 Rough E.R. #3 Ribosome's Cytoskeleton or Microfilaments #4 #5 Mitochondria