* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
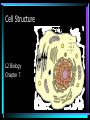
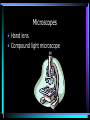
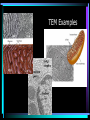
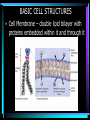
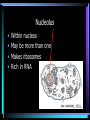
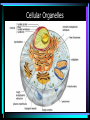
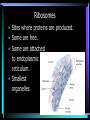
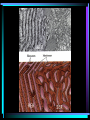
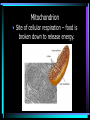
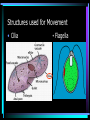
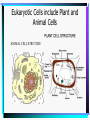
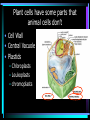
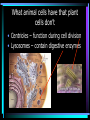
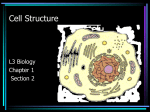
Cell Structure L2 Biology Chapter 7 What is a cell? • Smallest unit of life that can carry out all the functions of a living thing. • Various sizes and shapes • Organism- living thing – Unicellular – multicellular Microscope Development • 1500’s – first microscope developed • 1665 – Robert Hooke named cell • 1674 – Anton van Leeuwenhoek looked at cells in pond water and blood Cell Theory Developed • 1838 – Schleiden – all plants are made of cells • 1839 – Schwann – all animals are made of cells • 1855 – Virchow – all cells come from pre-existing cells Modern Cell Theory • Cells are the basic units of all life. • All organisms are made of one or more cells • All cells come from pre-existing cells Microscopes • Hand lens • Compound light microscope Electron Microscope • Uses electrons for energy source • Specimen must be killed • Transmission electron microscope – take pictures of slices of specimen • Scanning electron microscope – take pictures of surface of specimen TEM Examples SEM Example Cells from Labs: BASIC CELL STRUCTURES • Cell Membrane – double lipid bilayer with proteins embedded within it and through it Cytoskeleton • Cell support • Anchors organelles • Transports materials • Helps cell move Nucleus • Control center of cell • Contains genetic material – Chromosomes • Humans have 46 in each cell • Made of DNA - control heredity - control protein synthesis • Surrounded by double membrane – nuclear envelope – contains pores Nucleolus • • • • Within nucleus May be more than one Makes ribosomes Rich in RNA Types of Cells • Prokaryotic – Simple cell – No membrane-bound organelles – Chromosome not contained in nucleus – Small cells – Ex - bacteria • Eukaryotic – Complex cell – Membrane-bound organelles – Chromosomes contained in nucleus – Larger cells – Ex – all other organisms Cellular Organelles Ribosomes • Sites where proteins are produced. • Some are free. • Some are attached to endoplasmic reticulum. • Smallest organelles Endoplasmic Reticulum • Transport passages throughout cytoplasm • Rough ER – have ribosomes attached – Transport proteins – Helps make membranes • Smooth ER – no ribosomes attached – Makes lipids – Detoxifies wastes Golgi Apparatus • Packages cell secretions • Makes lysosomes – Contain digestive enzymes for breaking down food in food vacuoles – Contains digestive enzymes for breaking down un-needed structures – ex – sperm tail after fertilization. Mitochondrion • Site of cellular respiration – food is broken down to release energy. Structures used for Movement • Cilia • Flagella Eukaryotic Cells include Plant and Animal Cells ANIMAL CELL STRUTURE Plant cells have some parts that animal cells don’t • Cell Wall • Central Vacuole • Plastids – Chloroplasts – Leukoplasts – chromoplasts What animal cells have that plant cells don’t • Centrioles – function during cell division • Lysosomes – contain digestive enzymes Now you are ready to have a test on parts of a cell and what they do: Cell Part Cell membrane Cytoplasm Appear- Function ance In Animal In Plant cell cell In addition, you should be able to name some differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Make a chart like this: Feature Prokaryotic Eukaryotic THE END