* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Signaling pathway
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Hedgehog signaling pathway wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
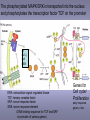
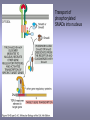
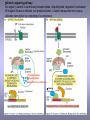
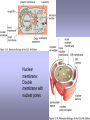
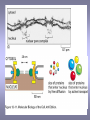
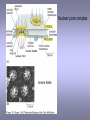
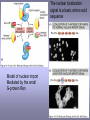
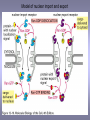
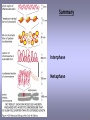
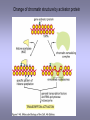
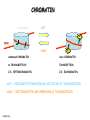
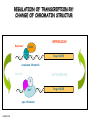
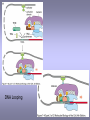
CELLULAR SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION 2) From the membrane to the nucleus TEIL F TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS AND THE REGULATION OF TRANSCRIPTION Rainer deMartin / Erhard Hofer Institute of Vascular Biology and Thrombosis Research Vienna Competence Center Lazarettgasse 19, 1090 Wien Erhard Hofer activation of transcription factors by surface receptors Summary selected examples CREB, SRF, NFAT, SMAD additional specific example: - Regulation of signaling pathways/transcription factors by proteolytic cleavage: WNT, NOTCH (embryonic development, adult stem cells) Nuclear import, -export Chromatin Transcription initiation complexes Rainer deMartin: Principals of transcriptional regulation Structural features of transcription factors Basic mechanisms of transcriptional regulation Signaling pathways: Receptor to transcription factors A-Cyclase PLC Ras SMAD STAT IKKK SMAD/Co-SMAD cAMP PKA NFAT / NFkB SRF STAT SMAD CREB, SRF, NFAT, SMAD Gene regulation by PKA: CREB bound to CRE Is phosphorylated by PKA, activates transcription without effect on DNA binding Example 3 The phosphorylated MAPK ERK is transported into the nucleus and phosphorylates the transcription factor TCF on the promoter or: PLC-g Raf MEK ERK: extracellular signal regulated kinase TCF: ternary complex factor SRF: serum response factor SRE: serum response element (DNA binding sequence for TCF and SRF in promoter of various genes) Genes for Cell cycle/ Proliferation early response genes, c-fos Ca++ Signaling pathway - Gene regulation the Phosphatase Calcineurin dephosphorylates NFAT NFAT translocates Into nucleus P I Ca++ NFAT Calmodulin Calcineurin P NFAT= transcription factor (nuclear factor activated T cell) Kern Transport of phosphorylated SMADs into nucleus Regulation of transcription factors by proteolytic cleavage WNT signaling pathway Secreted signaling peptide, important in embryonic development Mutatios on proteins of wnt signaling pathway frequent in cancer Example 4a Wnt Wingless (Drosophila) Int-1 (breast cancer oncogen) (detected experimentally by virus Integration) In signalling pathway: APC (adenomoteous polyposis coli) mutated in adenoma of colon and 80 % of colon cancer induces myc gene and proliferation b-Catenin signaling pathway: w/o signal: b-catenin is continously phosphorylated, ubiquitinylated, degraded in proteasom Wnt-signal: Kinase is inhibited, non-phosphorylated b-Catenin transported into nucleus, aktivates transcription by competing of a corepressor (LDL rceptor related protein) (Signaling protein) Phosphorylation, Ubiquitinylation, degradation in proteasom (Corepressor) (b-Catenin Coaktivator) components of the WNT signaling pathways e.g. important for maintaining the stem cell population in gastro-intestinal tract, Over-activation by APC mutation - cancer Notch example 5b hedgehog 1- Embryonic development E.g. nerve cells Drosophila, Delta on nerve cells signals to neighbouring cell: Do not differentiate to nerve cell, Peptide translocates into nucleus and converts CSL to become an activator 2- Angiogenesis: Tip versus stalk cell, tip cell signals stalk cell not to become another tip cell Nuclear import / -export Nuclear membrane: Double membrane with nuclear pores 26 nm Nuclear pore complex innere Seite The nuclear localization signal is a basic amino acid sequence Model of nuclear import Mediated by the small G-protein Ran Model of nuclear import and export CHROMATIN Summary Interphase Metaphase Eigenschaften von Insulatorelementen model Change of chromatin structure by activator protein CHROMATIN NUCLEOSOM HAT Ac DNA HDAC Ac condensed CHROMATIN loose CHROMATIN no TRANScRIPTION TRANCRIPTION Z.B. HETEROCHROMATIN Z.B. EUCHROMATIN HAT = HISTONACETYLTRANSFERASE ACTIVATOR OF TRANSCRIPTION HDAC = HISTONDEACETYLASE REPRESSOR of TRANSCRIPTION GENEXCS18 REGULATION OF TRANSCRIPTION BY CHANGE OF CHROMATIN STRUCTUR REPRESSION Repressor HDAC X Target GENE condensed Chromatin ACTIVIERUNG Aktivator Z Y A HAT open Chromatin GENEXCS19 Target GENE Gene regulatory proteins form frequently large complexes Mediator DNA Looping Gene expression