* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes (other NGS applications)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
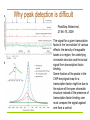
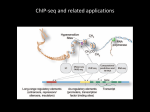
I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics, Fall, 2012 From ChIP-chip to ChIP-Seq: the study of mammalian transcription factor binding sites and epigenetics From Chip-Chip to Chip-Seq ChIP-chip (ChIP on tiled microarrays) ChIP-sequencing (ChIP-seq) combines chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and massively parallel sequencing to identify mammalian DNA sequences bound by transcription factors in vivo. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) between the side chains of two lysines between lysine & cytosine Formaldehyde (CH2O) is a very reactive dipolar compound (the carbon atom is the nucleophilic center). Amino and imino groups of proteins (e.g., the side chains of lysine and arginine) and of nucleic acids (e.g., cytosine) react with formaldehyde, leading to the formation of a Schiff base (reaction I) Chip-Seq workflow Solexa sequencing technology provided short read length sequences of approx 30 base pairs that were ideal for characterizing ChIP-derived fragments. Nature Methods - 4, 613 - 614 (2007) Advantages of ChIP-Seq Single base-pair resolution of direct sequencing ChIP-seq data are likely to have less noise or artifacts potential binding regions need not be specified prior to experiment lower cost, minimal hands-on processing and a requirement for fewer replicate experiments as well as less input material. Epigenetics meets next-generation sequencing. Epigenetics. 2008 Nov;3(6):318-21 Next generation sequencing (NGS) techniques 454 Sequencing Illumina/Solexa ABI SOLiD Sequencing Chemistry Pyrosequencing Polymerase-based sequence-bysynthesis Ligation-based sequencing Amplification approach Emulsion PCR Bridge amplification Emulsion PCR Paired end (PED) separation 3 kb 200-500 bp 3 kb Mb per run 100 Mb 1300 Mb 3000 Mb Time per PED run <0.5 day 4 days 5 days Read length (update) 250-400 bp 35, 75 and 100 bp 35 and 50 bp Cost per run $ 8,438 USD $ 8,950 USD $ 17,447 USD Cost per Mb $ 84.39 USD $ 5.97 USD $ 5.81 USD Tools for extracting transcription factor targets from ChIP-Seq data CisGenome uses a conditional binomial model to identify enriched regions when a control data set is provided (Nat. Biotechnol. 26:1293–1300, 2008) MACS (Model-based Analysis of ChIP-Seq) uses the control dataset to model the tag distribution across the genome using the Poisson distribution lBG (Genome Biol, 9:R137, 2009) PeakSeq enables systematic scoring of ChIP-seq experiments relative to controls (Biotechnol, 27:66–75, 2009) QuEST (Quantitative Enrichment of Sequence Tags) Nat. Methods, 5:829–834, 2008 GLITR (GLobal Identifier of Target Regions) identifies enriched regions in target data by calculating a fold-change based on random samples of control (input chromatin) data Why peak detection is difficult PeakSeq: Biotechnol, 27:66–75, 2009 The signal for a given transcription factor is the 'convolution' of various effects: the density of mappable bases in a region, the underlying chromatin structure and the actual signal from transcription factor binding. Some fraction of the peaks in the ChIP-seq signal map for a transcription factor might be due to the nature of the open chromatin structure instead of the presence of transcription factor binding--one must compare the signal against one from a control. PeakSeq scoring procedure Biotechnol, 27:66–75, 2009 High-Resolution Profiling of Histone methylations in the human genome Ref: Cell, 129(4):823-837, 2007 Generated high-resolution maps for the genome-wide distribution of 20 histone lysine and arginine methylations and others across the human genome using the Solexa 1G sequencing technology (The cells were digested with MNase to generate mainly mononucleosomes with minor fraction of dinucleosomes for histone modification mapping) Typical patterns of histone methylations exhibited at promoters, insulators, enhancers, and transcribed regions are identified. – The monomethylations of H3K27, H3K9, H4K20, H3K79, and H2BK5 are all linked to gene activation – trimethylations of H3K27, H3K9, and H3K79 are linked to repression. – H2A.Z (a Histone variant) associates with functional regulatory elements, and CTCF marks boundaries of histone methylation domains. – … BS-seq for epigenetic profiling BS-seq (bisulphite sequencing) combines bisulphite treatment of genomic DNA with ultrahigh-throughput sequencing Cytosine DNA methylation is important in regulating gene expression and in silencing transposons and other repetitive sequences Bisulphite sequencing References Genome-wide profiles of STAT1 DNA association using chromatin immunoprecipitation and massively parallel sequencing. Nature Methods - 4, 651 - 657 (2007)