* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The 7 Characteristics of Life
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
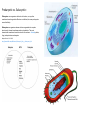
Cell Part Cell Wall Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria Chloroplast Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Golgi Apparatus Lysosome Vaculoe Function To provide structure and support to plant cells and some single celled organisms A phospholipid double layer that functions in the movement of materials in and out of the cell. It is selective about what passes the membrane. The jelly-like substance that function to hold all intercellular materials in place. It often refers to everything inside the cell except the nucleus. The nucleus is the membrane bound organelle that houses the genetic material of a Eukaryotic cell. The genetic material dictates the function and reproduction of cellular processes. The membrane bound organelle in Eukayotic cells where Respiration takes place. This means it is the location where energy is released for cellular activities. (looks like a bean with ribbons inside) Found only in photosynthetic organisms such as green plants, this structure is where photosynthesis is used for the production of glucose. (looks like a bean filled with pancakes) Often attached to the nucleus and is covered with dots (ribosomes), the ER functions as transportation hallways to more material around the cell. (smooth- no ribosomes, Rough- with Ribosomes) Manufacture proteins. They are found througout the cytoplasm and attached to the Rough ER. A structure that looks like a large stack of pancakes (no ribosomes). Its function is to package materials for cellular use. A digestive organnelle that processes waste. A storage unit in the cell. The cells function dictates what the vaculoe will hold. In plants it is usually water or starch. In human fat cells, the vaculoe would be filled with fat. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic: Prokaryotes are organisms without a cell nucleus, or any other membrane-bound organelles. Most are unicellular, but some prokaryotes are multicellular). Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells are organized into complex structures by internal membranes and a cytoskeleton. The most characteristic membrane bound structure is the nucleus. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are eukaryotes. Adapted from: 9-24-2013 http://www.diffen.com/difference/Eukaryotic_Cell_vs_Prokaryotic_Cell The 7 Characteristics of Life: 1. Living Things are Composed of Cells: Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, specialization increases until some cells do only certain things. 2. Living Things Have Different Levels of Organization: Both molecular and cellular organization. Living things must be able to organize simple substances into complex ones. Living things organize cells at several levels: Tissue - a group of cells that perform a common function. Organ - a group of tissues that perform a common function. Organ system - a group of organs that perform a common function. Organism - any complete living thing. 3. Living Things Use Energy: Living things take in energy and use it for maintenance and growth. 4. Living Things Respond To Their Environment: Living things will make changes in response to a stimulus in their environment. A behavior is a complex set of responses. 5. Living Things Grow: Cell division - the orderly formation of new cells. Cell enlargement - the increase in size of a cell. Cells grow to a certain size and then divide. An organism gets larger as the number of its cells increases. 6. Living Things Reproduce: Reproduction is not essential for the survival of individual organisms, but must occur for a species to survive. All living things reproduce in one of the following ways: Asexual repoduction - Producing offspring without the use of gametes. Sexual reproduction - Producing offspring by the joining of sex cells. 7. Living Things Adapt To Their Environment: Adaptations are traits giving an organism an advantage in a certain environment. Variation of individuals is important for a healthy species. Questions: 1. Do all living things have all of the characteristics of life? If your answer is no, give an example. 2. Name some non-living thing that uses energy. 3. Name some non-living thing that grows.