* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chromosome vs. Gene Mutations
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
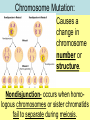
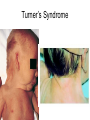
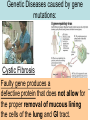
Aim: How can we compare chromosome mutations & gene mutations? Gene Chromosome Chromosome Mutation: Causes a change in chromosome number or structure. Nondisjunction- occurs when homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis. Trisomy Vs Monosomy: Trisomy 21 3 Copies of a Chromosome Down Syndrome Monosomy X 1 copy of a homologous pair Turner Syndrome Down Syndrome Turner’s Syndrome What causes nondisjunction to occur? Trisomy 21 No one really knows for sure, but the older the age of the mother the greater the chance of having a child with Down Syndrome. Chromosome Damage: Part of a chromosome is repeated. Part of a chromosome is missing. Reversing a fragment of the chromosome. Rearrangement of parts between nonhomologous pairs of chromosomes. Gene Mutations: • Are due to a change in a single gene. • Can involve changes in several nucleotides Genetic Diseases caused by gene mutations: Cystic Fibrosis Faulty gene produces a defective protein that does not allow for the proper removal of mucous lining the cells of the lung and GI tract. Gene Mutations: Tay-Sachs Disease Faulty gene produces a defective enzyme which cannot help remove fat from nerve cells. Sickle-Cell Anemia: One base is substituted for another and this causes the production of a distorted hemoglobin molecule (protein) which cannot function properly. What do these three gene mutations have in common? They all affect the shape of proteins!! If we change the shape of proteins (enzymes) they will not function properly and this will affect our phenotype.