* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell * The smallest functional and structural unit of all living
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
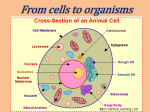
Cell * The smallest functional and structural unit of all living organisms Organism * Any living thing made up of cells Cell Membrane * A protective layer that covers a cell’s surface and acts as a barrier between the inside of a cell and the cell’s environment Cytoplasm * All the fluids and all of the organelles of the cell Organelle * A small body in a cell’s cytoplasm that is specialized to perform specific functions Nucleus * Contains the cell’s DNA * Has role in the processes such as growth, metabolism and reproduction DNA * Deoxyribonucleic acid is a genetic material that provides instructions for all cell processes. Prokaryote *A single celled organism that does not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Its DNA is located in the cytoplasm Flagella * Hair like structures that help prokaryotic cells move Eukaryote *An organism made up of cells that contain their DNA in the nucleus. Most are multi-cellular, but some such as amoebas and yeast are unicellular. Atom * The smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element Molecule * A group of atoms that are held together by chemical bonds; a molecule is the smallest unit of a compound that keeps all the properties of that compound Lipid *A fat molecule that has many jobs including storing energy. Examples include oils, waxes and steroids Protein *A molecule that is made up of amino acids and that is needed to build and repair body structures and to regulate processes in the body Carbohydrates * A class of molecules that includes sugars, starches, and fiber; contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen *Cells use them to release and to store energy. Nucleic Acid * A molecule that carries information in cells – made up of smaller molecules called nucleotides Nucleotides *In a nucleic-acid chain, a subunit that consists of sugar, a phosphate and a nitrogenous base Phospholipids * A lipid that contains phosphorus and that is a structural component in cell membranes *The head attracts water / The tail repels water Osmosis *The diffusion of water through a semi permeable membrane Cytoskeleton *Is a network of protein filaments that gives shape and support to the cells Mitochondrion * The site of cellular respiration, which releases energy for use by the cel Cellular Respiration * The process by which a cell uses oxygen to produce energy from food Ribosome * Makes protein by putting together chains of amino acids Endoplasmic Reticulum * A system of membranes that is found in a cell’s cytoplasm and that assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and makes lipids Photosynthesis * The process by which cells use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to make sugar and oxygen Chlorophyll * Green pigment Golgi complex * A cell organelle that helps make and package materials to be transported out of the cell Cell Wall *A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell Vacuole * A fluid filled vesicle found in the cytoplasm of plant cells or protozoan Chloroplast *Uses sunlight carbon dioxide and water to make food by photosynthesis Lysosome * Produces enzymes that digest wastes, cell parts and foreign invaders Organism *A living thing that can carry out life processes by itself Tissue *A group of similar cells that perform a common function Organ *A collection of tissues that carry out a specialized function of the body Organ System * A group of organs that work together to perform body functions Structure * The arrangement of parts in an organism Function * Activity of each part in an organism Xylem * Transports water from roots to cells Phloem * Transports nutrients made in leaf cells to all parts of the plant Homeostasis * The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment itosis M * A process of cell division – the nucleus splits to form two identical nuclei Passive Transport * The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell Diffusion *The movement of particles from regions of higher density to regions of lower density Active Transport * The movement of substance across the cell membrane that requires cell to use energy Endocytosis * The process by which a cell membrane surrounds a particle and enclose the particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell Exocytosis * The process in which a cell releases a particle by enclosing the particle in a vesicle that moves to the cell surface and fuses with the cell membrane Glucose *Is a sugar that stores chemical energy