* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Warm-ups Life Science
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
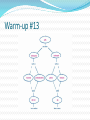
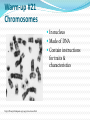
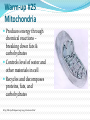
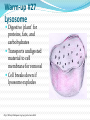
Quarter 1 Warm-up #1 What is Life Science? (take a guess if you do not know) Warm-up #1 What is Life Science? The life sciences comprise the fields of science that involve the scientific study ofliving organisms, such as microorganisms, plants, animals, and human beings. The study of LIFE!!!!! Warm-up #2 Characteristics Of Living Things They have cells They sense and respond to change They reproduce They have DNA They use energy They grow and develop Warm-up #3-copy this adaptation Definition: The process by which a living organism conforms to its environment Context: A species� adaptations over time improve its chance of survival. organisms Definition: Any living things that can act or function independently Context: Organisms live in the upper levels of the atmosphere and deep in the oceans. Warm-up #4- copy this photosynthesis Definition: Process through which light energy, water, and carbon dioxide are converted to carbohydrate and oxygen in the presence of chlorophyll Context: To be classified as a plant, an organism makes its own food through photosynthesis. species Definition: A classification of related living organisms that can freely interbreed without complications Context: The bald eagle was once an endangered species. taxonomy Definition: The science of classifying plants and animals into species and logical groups of species Context: Scientists use taxonomy to group living organisms. Warm-up #5 copy this Warm-up #6 What are microscopes? Noun An optical instrument used for viewing very small objects, typically magnified several hundred times. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X-w98KA8UqU Warm-up # 7 What Is Cell Biology? Cell biology is the subdiscipline of biology that studies the basic unit of life, the cell. It deals with all aspects of the cell including cell anatomy, cell division (mitosis and meiosis), and cell processes such as cell respiration, and cell death. Cell biology does not stand alone as a discipline but is closely related to other areas of biology such as genetics, molecular biology, and biochemistry. Warm-up #8 Cells and the Cell Theory • Finding Cells in Other Organisms In 1673, Anton van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch merchant, made his own microscopes. Leeuwenhoek was the first person to see bacteria. And he discovered that yeasts that make bread dough rise are single-celled organisms. • The Cell Theory All organisms are made of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of all living things. All cells come from existing cells. Warm-up #9 Cells • A Few Large Cells Most cells are small. A few, however, are big. A chicken egg is one big cell. • Many Small Cells There is a physical reason why most cells are so small. Cells take in food and get rid of wastes through their outer surface. As a cell gets larger, it needs more food and produces more waste. Therefore, more materials pass through its outer surface. As the cell’s volume increases, its surface area grows too. Learn how to calculate a cells surface area-to-volume ratio in the next slide. Warm-up #10 Parts of a Cell • The Cell Membrane and Cytoplasm The cell membrane is a protective layer that covers the cell’s surface and acts as a barrier. Inside the cell is a fluid called cytoplasm. • Organelles Organelles are structures that perform specific functions within the cell. • Genetic Material DNA is the genetic material that carries information needed to make new cells and new organisms. Warm-up #11 Two kinds of Cells With or Without a Nucleus There are two basic types of cells— cells without a nucleus and cells with a nucleus. Warm-up #12 • What Are Eukaryotes? Organisms made of eukaryotic cells are called eukaryotes. • The Cell Theory Eukaryotic cells are the largest cells. Unlike bacteria and archaebacteria, eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. You can see other parts of a typical eukaryotic cell on the next slide. Warm-up #13 Warm-up #14 Name all the parts of the Animal Cell? (hint use Worksheet) Warm-up #15 Name all the parts of the Plant Cell? (hint use Worksheet) Warm-up #16 Organelles The human body contains many different organs, such as the heart, lung, and kidney, with each organ performing a different function. Cells also have a set of "little organs", called organelles, that are adapted and/or specialized for carrying out one or more vital functions. Organelles are found only in eukaryotes and are always surrounded by a protective membrane. It is important to know some basic facts about the following organelles. Warm-up #17 The Cell Theory states :All living organisms are composed of cells. They may be unicellular or multicellular. The cell is the basic unit of life. Cells arise from pre-existing cells. Warm-up #18 Cell Membrane Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell Double layer http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Warm-up #19 Cell Wall Most commonly found in plant cells & bacteria Supports & protects cells http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Warm-up #20 Nucleus Directs cell activities Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane Contains genetic material - DNA Warm-up #21 Chromosomes In nucleus Made of DNA Contain instructions for traits & characteristics http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Warm-up #22 Cytoplasm Gel-like mixture Surrounded by cell membrane Contains hereditary material Warm-up #23 pho·to·syn·the·sis ˌfōtōˈsinTHəsis/ noun 1. the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods from carbon dioxide and water. Photosynthesis in plants generally involves the green pigment chlorophyll and generates oxygen as a byproduct. Warm-up #24 Endoplasmic Reticulum Moves materials around in cell Smooth type: lacks ribosomes Rough type (pictured): ribosomes embedded in surface http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Warm-up #24 Ribosomes Each cell contains thousands Make proteins Found on ribosomes & floating throughout the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Warm-up #25 Mitochondria Produces energy through chemical reactions – breaking down fats & carbohydrates Controls level of water and other materials in cell Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Warm-up #26 Golgi Bodies Protein 'packaging plant' Move materials within the cell Move materials out of the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Warm-up #27 Lysosome Digestive 'plant' for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Warm-up #28 Vacuoles Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal Contains water solution Help plants maintain shape http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Warm-up #29 Chloroplast Usually found in plant cells Contains green chlorophyll Where photosynthesis takes place http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html