* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download New roles for RNA
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
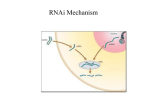
New roles for RNA New fields for bioinformatics? Morten Lindow Centre for Bioinformatic University of Copenhagen RNA modul • Torsdag – Forelæsning • ncRNA, RNAi, miRNA – Opgave gennemgang, Bioperl, næste hjemmeopgave • Tirsdag – Morgen: Øvelse – lave færdig, snakke snakke. – Eftermiddag: Opsamling • Foredrag: mit projekt Øvelser • Formål: – Få basal øvelse i at håndtere sekvenser i perl – Værdsætte BioPerl – Prøve at finde miRNA i Arabidopsis Plan for this lecture • Abundance of ncRNA • Types of ncRNA • RNAi – discovery and mechanisms – miRNA • RNAi as a technology • RNAi – the genome’s immune system • ncRNA and chromatin What is the difference? Source of variation • What is the homology of protein coding genes between human and mice? – 99 % !!!!!! • There are ~3 000 000 nucleotide differences between two humans. – 10 000 in protein coding genes (0.03%) • Most are silent (third base) • So where do the phenotypic differences between two individuals or two species come from? Source of differences? • Whole system properties: – Variations in gene expression (time/space). • Control architecture is the primary source of complex traits variation – Background for • Intercellular communication & integration • Interorgan communication & integration • Interindividual communication & integration Systems biology Control Architecture Genome Regulation by proteins Transcriptome Proteome Regulation by RNA Types of RNA RNA mRNA rRNA Ribosomal RNA Participate in protein synthesis tRNA Transfer RNA Interface between mRNA & amino acids ncRNA Non-coding RNA. Transcribed RNA with a structural, functional or catalytic role snRNA snoRNA Small nuclear RNA Small nucleolar RNA -Incl. RNA that Found in nucleolus, form part of the involved in modification spliceosome of rRNA miRNA Micro RNA Small RNA involved regulation of expression Other Including large RNA with roles in chromotin structure and imprinting siRNA stRNA Small temporal RNA. RNA with a role in developmental timing Small interfering RNA Active molecules in RNA interference Discovery of RNAi • Conventional antisense: – ~50% downregulation • Fire et al. : Synergy when given together with sense RNA Examples of RNAi GFP expressed in nuclei Control dsRNA GFP specific dsRNA Red = silencing of GFP hairpin against pigment RNA interference RNAi mechanism RNase III like enzyme Endogenous vs exogenous Inhibition of translation Imperfect match Block translation Near-perfect match Degrade mRNA Defense against transposons? • In C.elegans and Drosophila mutation of RNAi components activation of transposons • Is RNAi a genomic immune system? – The vertebrate adaptive immune system: • Distinquish self from non-self • Amplify a response • Kill the intruder Genomic immune system hypothesis 1 • Self/non-self discrimination (generation od dsRNA) – Multicopy transposons: • read through from flanking promotors create complementary strands to form dsRNA – Some transposons have terminal inverted repeats hairpin Genomic immune system hypothesis 2 • Amplification of signal: – siRNA may work as primers on the mRNA • Amplification by RNA dependent RNA polymerase • (only detected in plants & yeast) Control Architecture Genome RNAi Regulation by proteins Transcriptome Proteome Regulation by RNA Regulation of transcription • What governs when a stretch of DNA is transcribed? – Transcription factors – Accessabilitity of DNA to transcription factors • Structure of the chromatin – Proteins – RNAs........ DNA & chromosome structure Movie Transcription and chromatin structure • Euchromatin – open structure – transcriptionally active • Heterochromatin – closed structure – silenced • Structure determined by – > methylation of cytosines histone binding Spread of DNA methylation Silent chromatin & RNAi • Centromers contain repeats and are often heterochromatic (silenced) •Finding: Deletion of RNAi machinery causes desilencing centromeric regions CREDIT: KATHARINE SUTLIFF/SCIENCE Control Architecture Imprinting – methylation Splicing Genome RNAi Regulation by proteins Transcriptome Proteome Regulation by RNA Ribozymes Why use RNA in regulation? • Less cost – Genomic space. Compare RNA vs protein – Metabolic space. Cost of aminoacids • Speed – RNA produced and active very quickly • Easier to evolve. Less costly to explore ’expression space’ So why proteins? • More adaptable • Better at sensing environment – responding to signal transduction etc