* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY Citric Acid Cycle
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
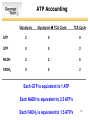
SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY Citric Acid Cycle 1 Formation of Acetyl CoA Acetyl CoA is a metabolic intermediate that can be produced from amino acids, glucose (via pyruvate), and fatty acids This rxn is the first of 5 dehydrogenase reactions. Here oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA (and reduction of NAD+ to NADH) leads to the production of CO2. 2 Formation of Citrate Citrate is a tricarboxylic acid. The citric acid cycle is sometimes referred to as the Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) Cycle. 3 Formation of Isocitrate Notice that aconitase catalyzes this reaction in both directions! 4 Formation of Alpha-Ketoglutarate Notice that the carbon that is cleaved off of isocitrate did not come from the carbons in acetyl CoA! This rxn is the second of 5 dehydrogenase reactions. 5 Formation of Succinyl-CoA This rxn is the third of 5 dehydrogenase reactions. Here a 5-C molecule is converted into a 4-C precursor. 6 Formation of Succinate GTP is equivalent to an ATP in terms of the energy yield from hydrolysis. 7 Formation of Fumarate This rxn is the fourth of 5 dehydrogenase reactions. FAD is the redox cofactor used by succinate dehydrogenase. 8 Formation of L-Malate 9 Formation of Oxaloacetate This rxn is the fifth of 5 dehydrogenase reactions. Oxaloacetate has now been regenerated so that it can react with a new molecule of acetyl CoA to repeat the cycle. 10 ATP Accounting Glycolysis Glycolysis TCA Cycle TCA Cycle ATP 2 0 0 GTP 0 0 2 NADH 2 2 6 FADH2 0 0 2 Each GTP is equivalent to 1 ATP Each NADH is equivalent to 2.5 ATP’s Each FADH2 is equivalent to 1.5 ATP’s 11 ATP Accounting TOTAL ATP 2 ATP Equivalents 2 GTP 2 2 NADH 10 25 FADH2 2 3 One molecule of glucose gets metabolized into ~32 ATP’s Each GTP is equivalent to 1 ATP Each NADH is equivalent to 2.5 ATP’s Each FADH2 is equivalent to 1.5 ATP’s 12 Summary • Read Chapter 17.1-17.4 • Learn each step of the TCA Cycle – – – – Substrates Products Reactants Cofactors • Next Monday – Mechanisms in the TCA Cycle – Control of the TCA Cycle 13