* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
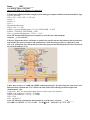
Name:_______KEY___________ Cell Biology Quiz#3: 20 points Answer any FOUR of the following Five Questions: 1) What is the optimal yield when a single pyruvate undergoes complete oxidation in the mitochondria? 5 pts Cytosolic Reactions: GTP or ATP= 4ATP-2ATP = 2 ATP yield NADH= 2 FADH2= 0 CO2= 0 Mitochondrial Reactions: GTP or ATP= 1 = 1 GTP NADH= (1 pyruvate dehydrogenase+ 3 TCA) X 3ATP/NADH = 12 ATP FADH2= 1 FADH2 X 2ATP/FADH2 = 2ATP CO2= (1 pyruvate dehydrogenase + 2 TCA) = 3 CO2 Total ATP Produced following electron transport by all of the above mitochondrial reactions:___1+12+2=15ATP 2) Draw a diagram that shows with names or numbers the specific enzymes and pathways that feed electrons from FADH2 into electron transport and chemiosmosis? About how many protons are required for each ATP to be synthesized? Show the chemical reaction that represents the final destination for these electrons at the end of the pathway? 5 pts 3) How many acetyl-CoA, NADH and FADH2 would be produced if a 18 carbon long fatty acid (stearic acid underwent beta-oxidation and TCA? What is the total yield of ATP following electron transport and chemiosomosis? 5 pts Acetyl-CoA= Nine (18 carbon chain makes nine two carbon acetyl-CoA molecules) NADH= 8 (B-oxidation)+ 27 (TCA) = 35 NADH FADH2= 8 (B-oxidation) + 9 (TCA) = 17 FADH2 GTP= 9 TCA CO2= 18 total TCA Total ATP following chemiosmosis made possible by all of the above reactions:_____148_______ 35 NADH X 3= 105 ATP 17 X 2 = 34 ATP 9 GTP9ATP Total=105 + 34 + 9 = 1 ATP 4) Compare and Contrast the Structure and Function of a mitochondria and a chloroplast with respect to number of membranes, names of structures, directions of proton gradients, and the use of NAD/NADP (5 points). Mitochondria and Chloroplast both contain DNA of prokaryotic origins, they both generate proton gradients and they both use a ATP-synthase that is dependent on a proton gradient. Mitochondria contain two phospholipid bilayers (outer is porous, inner is very selective, 4 PL monolayers). They use energy from electron transport H+ out of matrix to the cristae, with oxygen as the final e- acceptor. The H+ leak back into the matrix through the ATP-synthase, such that the negative delta G is used to synthesize ATP (ADP+PiATP). In contrast, the chloroplast contains THREE PL bilayer (6 PL monolayers). The trick is that they use energy from light to excite electrons (Photosystem II) to strip an electron from water to create O2. The energy in the electron is used drive proton pumps that push H+ into the lumen of the thylakoid discs making them acidic on the inside. The protons are allowed to leak back out of the thylakoid discs (run down their conc. Gradients) by passing through an ATP-synthase (ADP+Pi ATP). The electrons are re-excited by light (Photosystem I) such that the final step is the production of NADPH (not NADH). 5) Compare and Contrast the Light and Dark Reactions with regards to their reactants, products, and their requirements for photons of light or ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (5 points) The light reactions require light to remove an electron from water to make oxygen in Photosystem II, then use the energy to create a proton gradient that is used to generate ATP, then use additional light to re-excite the electron in photosystem I and ultimately create NADPH. These reactions stop in the absence of light. The Dark reactions use accumulated ATP and NADPH to fix three carbon dioxides to pre-existing three ribulose1,5-bisphosphate (3X5-carbons) and create six 3-phosphoglycerates (6X 3carbons=18 carbons). For every six 3PGs created by carbon fixation, one glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G-3-P) or dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHP) can be produced and removed from the system such that the original three ribulose-1,5-bisphosphates can be regenerated. When G-3-P and DHP accumulate the delta G favors the synthesis of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and gluconeogenesis permits the fixed carbons to be convereted to glucose, starch or what ever the plant needs. The key is that carbon fixation ONLY occurs if pre-existing ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate is ready to accept it. Extra Credit) Consider TCA, name all the enzymes, and draw each structure for all products/reactants that permit one pyruvate to become oxidized in TCA. (2 points) TCA only occurs in the mitochondria-Glycolysis/gluconeogensis only occurs in the cytosol Remember that the Delta G values for a set of half reactions are only additive if they occur in the same intracellular compartment (no membranes in between), hence what happened in the cytosol for glycolysis and additive delta G is not additive to what happened in the mitochondria.