* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LW Global Warming Talk
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
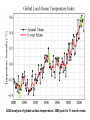
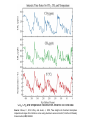
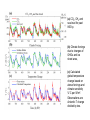
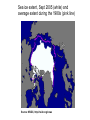
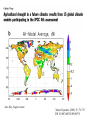
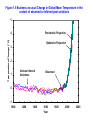
Climate Threat to the Planet:* Implications for Energy Policy and Intergenerational Justice Jim Hansen December 17, 2008 Bjerknes Lecture, American Geophysical Union San Francisco, California *Any Policy-Related Statements are Personal Opinion Global Warming as a Moral Issue L.D. Danny Harvey Department of Geography University of Toronto [email protected] GISS analysis of global surface temperature; 2008 point is 11-month mean. Surface temperature anomaly relative to base period 1951-1980. Left: Anomaly for 2008 meteorological year (December-November). Right: Anomaly for first seven years of this century. Basis of Understanding 1. Earth’s Paleoclimate History 2. On-Going Global Changes 3. Climate Models (note: modeling #3, but aids other two) Climate Change Depends on (global, averaged over chaos) 1. Equilibrium Climate Sensitivity 2. Forcings: Human & Natural 3. Response Time (Ocean Inertia) CO2, CH4 and temperature records from Antarctic ice core data Source: Vimeux, F., K.M. Cuffey, and Jouzel, J., 2002, "New insights into Southern Hemisphere temperature changes from Vostok ice cores using deuterium excess correction", Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 203, 829-843. (a) CO2, CH4 and sea level for past 800 ky. (b) Climate forcings due to changes of GHGs and ice sheet area, (c) Calculated global temperature change based on above forcings and climate sensitivity ¾°C per W/m2. Observations are Antarctic T change divided by two. Empirical Climate Sensitivity 3 ± 0.5C for 2XCO2 1. Includes all fast-feedbacks* *water vapor, clouds, aerosols, surface albedo (Note: aerosol feedback included) 2. Paleo yields precise result 3. Relevant to today’s climate sensitivity generally depends on climate state Climate Threat to the Planet The Venus Syndrome Runaway Greenhouse Effect? 1. Unprecedented Speed of +Forcing 2. Negative Feedbacks (e.g. Increased Weathering Rate) of Little Help 3. Solar Irradiance has Increased My Opinion: All Coal ?? (Runaway Possible) Coal + Tars !! (Dead Certainty) United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change Aim is to stabilize greenhouse gas emissions… “…at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system.” Metrics for “Dangerous” Change Extermination of Animal & Plant Species 1. Extinction of Polar and Alpine Species 2. Unsustainable Migration Rates Ice Sheet Disintegration: Global Sea Level 1. Long-Term Change from Paleoclimate Data 2. Ice Sheet Response Time Regional Climate Disruptions 1. Increase of Extreme Events 2. Shifting Zones/Freshwater Shortages Tipping Point Definitions 1. Tipping Level - Climate forcing (greenhouse gas amount) reaches a point such that no additional forcing is required for large climate change and impacts 2. Point of No Return - Climate system reaches a point with unstoppable irreversible climate impacts (irreversible on a practical time scale) Example: disintegration of large ice sheet Sea level rise – 20 cm since 1880 Source: IPCC 2007, AR4, WG1 Sea ice extent, Sept 2005 (white) and average extent during the 1980s (pink line) Source: NSIDC, http://nsidc.org/news Sea ice extent, Sept 2007 Source: National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), USA, http://nsidc.org/news Sea ice extent, Sept 2009 Source: NSIDC, http://nsidc.org/news Surface Melt on Greenland Melt descending into a moulin, a vertical shaft carrying water to ice sheet base. Source: Roger Braithwaite, University of Manchester (UK) Jakobshavn Ice Stream in Greenland Discharge from major Greenland ice streams is accelerating markedly. Source: Prof. Konrad Steffen, Univ. of Colorado Rongbuk Glacier Rongbuk glacier in 1968 (top) and 2007. The largest glacier on Mount Everest’s northern slopes feeds Rongbuk River. Areas of the world dependent on winter snowfall for summer moisture: Shown is the ratio of annual snowfall to annual runoff. The red line outlines the areas where runoff is predominantly from snowmelt and there is not adequate storage to buffer seasonal variations. Source: Barnett et al (2005) Pier on Lake Mead Subtropics expected to expand with global warming. Observations show 4 degrees of latitude expansion. Fires Are Increasing World-Wide Wildfires in Western US have increased 4-fold in 30 years. Western US area burned Source: Westerling et al. 2006 Stresses on Coral Reefs Coral Reef off Fiji (Photo: Kevin Roland) Source: Nature 442, 978-980 (2006) Assessment of Target CO2 Phenomenon Target CO2 (ppm) 1. Arctic Sea Ice 300-325 2. Ice Sheets/Sea Level 300-350 3. Shifting Climatic Zones 300-350 4. Alpine Water Supplies 300-350 5. Avoid Ocean Acidification 300-350 Initial Target CO2 = 350* ppm *assumes CH4, O3, Black Soot decrease Target CO2: < 350 ppm To preserve creation, the planet on which civilization developed Initial Target CO2: 350 ppm Technically Feasible (but not if business-as-usual continues) Quick Coal Phase-Out Critical (long lifetime of atmospheric CO2) (must halt construction of any new coal plants that do not capture & store CO2) Damage-control Scenarios 7.0 6.0 Damage-control, Unlucky Case o Global Average Warming ( C) Business-as-Usual, Unlucky Case 5.0 Business-as-Usual, Lucky Case 4.0 3.0 2.0 Observed 1.0 Damage-control, Lucky Case 0.0 -1.0 1850 1900 1950 2000 Year 2050 2100 Figure 1.5 Business as usual Change in Global Mean Temperature in the context of observed or inferred past variations 5 Pessimistic Projection Optimistic Projection o Temperature Change ( C) 4 3 2 1 Various Inferred Variations Observed 0 -1 1000 1200 1400 1600 Year 1800 2000 2200 The Challenge We can avoid destroying creation! (+cleaner planet, + good jobs!) We have to figure out how to live without fossil fuels someday… Why not now? Carbon Tax & 100% Dividend 1. Tax Large & Growing (but get it in place!) - tap efficiency potential & life style choices 2. Entire Tax Returned - equal monthly deposits in bank accounts 3. Limited Government Role - keep hands off money! - eliminate fossil subsidies - let marketplace choose winners - change profit motivation of utilities - watch U.S. modernize & emissions fall! Intergenerational Conflict Intergenerational inequity and injustice is the result, affecting the young and unborn. ‘Did not know’ defense of prior generations no longer viable. Ethical and legal liability questions raised by actions that deceived the public. Continued failure of political process (not even available to young and unborn) may cause increasing public protests. Major Impacts of Concern • Sea level rise of 6-12 m over several centuries to a 1000 years or more • Increased occurrence of drought • Increased water stress in vulnerable regions • Species extinction (1/3 to ½ this century) • Acidification of the oceans Moral and Ethical Dimensions • The sanctity of life • Disproportionate impacts on the most vulnerable (poor people) and on developing countries – those least responsible, and least able to adapt • Intergenerational impacts, discounting • Imposition of involuntary risk on others What Will it Take? • Stabilization of the human population at the lowest possible level (i.e., 8 billion instead of 10 billion or more) • An end to the growth-for-the-sake-of-growth paradigm • Massive emphasis on energy efficiency and conservation (an efficiency and sufficiency ethic) • Massive acceleration in the deployment of renewable energy sources Personal Decisions with Moral Implications • Use of energy (especially concerning transportation, home heating and cooling, energy-intensive conveniences) • Levels of consumption (how much “stuff” are you buying?) • The amount of meat in your diet • The levels of convenience and comfort that you demand Moral Behaviour is • To be happy with less • To consume less • To tread as lightly as possible on the planet • To make “sacrifices” cheerfully (Ghandi)