* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE CELL
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
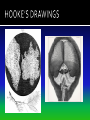
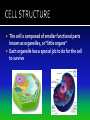
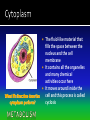
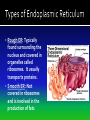
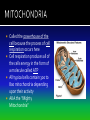
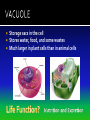
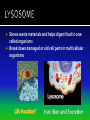
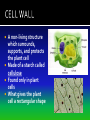
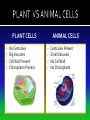
The discovery of cells occurred only after the development of the microscope In the 1600s, Anton Van Leeuwenhoek developed the single lens microscope and discovered: Living organisms in water Red Blood Cells Bacteria Robert Hooke developed a more modern microscope and used it to examine cork He observed tiny individual units within the cork that he called “cells” because it reminded him of monks’ cells After years of research, scientists summarized their findings into three statements. Together, they make up the cell theory: 1. All living things are made up of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function of all living things 3. All cells come from preexisting cells The cell is composed of smaller functional parts known as organelles, or “little organs” Each organelle has a special job to do for the cell to survive Surrounds the cell and controls the movement of materials both into and out of the cell It is considered “semi-permeable”- some materials can pass through and some cannot The fluid-like material that fills the space between the nucleus and the cell membrane It contains all the organelles and many chemical activities occur here It moves around inside the cell and this process is called cyclosis “Brain of the Cell” Controls all the life functions of the cell Surrounded by a nuclear membrane Inside are chromosomes, which are made of long thin threads call chromatin Chromatin contains DNA, the cell’s hereditary material Found inside the nucleus Involved in the synthesis of ribosomes A network of channels or canals that transports substances made in the cell Two Types: Rough ER Smooth ER Rough ER: Typically found surrounding the nucleus and covered in organelles called ribosomes. It usually transports proteins. Smooth ER: Not covered in ribosomes and is involved in the production of fats Carry out protein synthesis They can be free floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum Called the powerhouse of the cell because the process of cell respiration occurs here Cell respiration produces all of the cells energy in the form of a molecule called ATP All typical cells contain 300 to 800 mitochondria depending upon their activity AKA the “Mighty Mitochondria” “Stacks of Sacs” Serve as storage centers for the cell They store, sort, and package proteins. These packages then move to the cell membrane where the proteins are released to outside the cell Storage sacs in the cell Stores water, food, and some wastes Much larger in plant cells than in animal cells A full vacuole puts pressure on the sides of the cell wall and keeps the plant cell rigid and strong, and the plant standing upright When a plant loses water, the vacuoles shrink, and the plant cells shrivel, making the plant appear wilted Stores waste materials and helps digest food in onecelled organisms Break down damaged or old cell parts in multicellular organisms Pair of cylinder-shaped structures found just outside the nucleus that aid in cell division Only found in animal cells A non-living structure which surrounds, supports, and protects the plant cell Made of a starch called cellulose Found only in plant cells What gives the plant cell a rectangular shape Found only in plant cells Contain the green pigment chlorophyll Carry out the process of photosynthesis, which is how green plants make their own food PLANT CELLS No Centrioles Big Vacuoles Cell Wall Present Chloroplasts Present ANIMAL CELLS Centrioles Present Small Vacuoles No Cell Wall No Chloroplasts 1. If all cells come from pre-existing cells, where did the first cell come from? It must have come from non-living material 2. Viruses are not made up of cells, but contain genetic material. The only cellular activities that they carry on are synthesis and reproduction inside a living cell 3. Certain cell organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, contain their own genetic material and can reproduce independently in the cell