* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transport in cells - Durrington High School
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
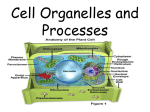
Transport in cells Target:………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… /27 Key words and definitions Diffusion – the spreading out of the particles of any substance in a solution or gas resulting in the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration down a concentration gradient. Osmosis – the diffusion of water through a partially permeable membrane from a dilute solution (high concentration of water) to a concentrated solution (low concentration of water) down a concentration gradient. Partially permeable membrane – a membrane that allows only certain substances to pass through. Isotonic – a solution that is the same concentration as the cell contents. Hypertonic – a solution that is more concentrated than the cell contents. Hypotonic – a solution that is less concentrated than the cell contents. Turgor – the pressure inside a plant cell exerted by the cell contents pressing on the cell wall. Plasmolysis – the state of plant cells when so much water is lost from the cell by osmosis that the vacuole and cytoplasm shrink and the cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall. Active transport – the movement of substances from a dilute solution to a more concentrated solution against a concentration gradient, requiring energy from respiration. Ventilated – movement of air or water into and out of the gas exchange organ, eg lungs or gills. Alveoli – tiny air sacs in the lungs that increase the surface area for gaseous exchange. Stomata – openings in the leaves of plants, particularly on the underside and opened and closed by guard cells, allowing gases to enter and leave the leaf. 1. Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (1) (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration of oxygen in three cells, A, B and C. Diagram 1 Oxygen can move from cell to cell. Into which cell, A, B or C, will oxygen move the fastest? ………………….. (1) (b) (i) How does water move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. breathing osmosis respiration (1) (ii) Differences in the concentration of sugars in cells cause water to move into or out of cells at different rates. Diagram 2 shows three different cells, P, Q and R. The information shows the percentage concentration of sugar solution in cells P, Q and R. Diagram 2 Water can move from cell to cell. Into which cell, P, Q or R, will water move the fastest? ……………….. Q2. (1) The drawing shows part of a root hair cell. (a) Use words from the list to label the parts of the root hair cell. cell membrane cell wall cytoplasm nucleus vacuole (4) (b) The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules. The cell is respiring aerobically. Which arrow, A, B, C or D represents: (c) (i) movement of oxygen molecules; (ii) movement of carbon dioxide molecules? .................... .................... (2) Name the process by which these gases move into and out of the cell. .............................................................................................................................. (1) Q3. The image below shows part of a plant root. The plant root is adapted for absorbing water from the soil. (a) Use information from the diagram to explain how this plant root is adapted for absorbing water. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................ (3) (b) How do the following features of plant roots help the plant to absorb mineral ions from the soil? (i) A root hair cell contains many mitochondria. .................................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Many of the cells in the root store starch. .................................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................................... (1) Q4. Read the following information about how the small intestine absorbs sugars. • • • • The blood absorbs glucose and some other sugars, like xylose, from the small intestine. Glucose molecules are the same size as xylose molecules, but glucose is absorbed more quickly than xylose. Experiments with pieces of intestine show that the uptake of oxygen by the intestine is 50 % higher in the presence of glucose than in the absence of glucose. Xylose does not have this effect on the uptake of oxygen. The cells lining the small intestine have many mitochondria. Explain how this information provides evidence that glucose is absorbed by the small intestine using active transport. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (4) Q5. The human lung has about 80 million alveoli. The diagram shows some alveoli in a human lung. (a) Give three features of the alveoli that allow large amounts of oxygen to enter the blood. 1 ............................................................................... 2 ............................................................................... 3 ............................................................................... (3) (b) (i) Name the process by which oxygen passes from the air into the blood. ............................................................................................................... (ii) (1) Breathing allows large amounts of oxygen to enter the blood. Explain how breathing does this. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2)