* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NAME
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
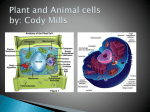
NAME:_________________________ PERIOD:________ DATE:________________ Bio Midterm exam review -2015 Chapter 1- Intro to Bio 1) What is biology? Study of life 2) What are the five characteristics of all living things? Dna,, cells, reproduce, grow and develop, homeostasis, evolve, obtain and use energy 3) What is a species? A group of organisms that can mate and produce fertile offspring 4) What is the order of the scientific method? Identify examples of each step. Observation, question, hypothesis, experiment, analysis, conclusion 5) Where does almost all energy come from? sun 6) What is a hypothesis? How is it related to a theory? Explanation/answer to a questions that can be tested 7) Describe how to set up a controlled experiment. Control group and experimental group, both receive all the same variables except one, the experimental group gets the independent variable and the control group does not. Control is there for comparison 8) What are some desirable characteristics of scientists? Skepticism, open mindedness, curiosity. Creativity 9) How does peer review help scientists? Helps find mistakes and learn from each other Chapter 2- Chemistry of Life 1) What are the parts of an atom and their charges and where are they found? Proton- positive, electron-negative , neutrons- neutral , protons and neutrsn in the nucleus of the atom 2) What is an element? A pure substance that cannot be broken down into smaller parts and maintain its characteristics 3) Be able to calculate the mass number and atomic number. Atomic #= # protons, mass #- #protons + #neutrons 4) Explain what an isotope is. An element that has more or less neutrons, but the same # protons 5) Describe how ions form. When an atom gains or loses an electron it forms an ion 6) Differentiate between polar and nonpolar molecules. Polar molecules have a + and - end, nonpolar= no charge, polar and nonpolar do not mix 7) Differentiate between the three types of bond Hydrogen-weak force between polar molecules Covalent- strongest –atoms share electrons Ionic- atoms bonded together by gaining or losing electrons 8) Identify the 4 organic compounds: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids 9) Describe 3 Properties that make water a unique substance Polar- cohesion, adhesion, capillary action Universal solvent- dissolves High heat capacity- water takes a long time to heat up and cool off 10) Identify products and reactants Reactants- in , products- out 11) Describe the pH scale A measure of the amount of hydrogen in a substance Scale is 0-14 , acids 0-7, 7- 14 base. 7 is neutral, acids have more hydrogen ions, bases have more hydroxide ions 12) What happens to atoms in a chemical reaction? Thet get rearranged 13) Explain how enzymes work Speed up chemical reactions by reducing the amount of activation energy needed to start the reaction 14) What factors affect enzyme action and how Temperature, pH Chapter 7- sections 1-2 Cell structure 1) What is the metric system based on?. Powers of 10 2) What is the smallest unit of life? cell 3) Differentiate between a prokaryote and a eukaryote Pro- no nucleus (bacteria) Euk- true nucleus 4) Know the functions of the cell membrane and what it is composed of. Supports the cell, Controls what goes in and out of a cell, phospholipid bilayer 5) Identify the organelles in a eukaryote and their functions. Nucleus, Er, ribosomes, mitochondria, Golgi, cytoplasm, vesicles, lysosomes, cell membrane, cell wall, vacuole, chloroplast 6) Differentiate between animal and plant cells Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplast. central vacuole, animal cells do not 7) Trace the production of a protein through the organelles of a cell. Nucleus, ER, ribosomes, golgi, vesicles 8) The three parts of the cell theory Living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, new cells come from existing cells Chapter 7 section 3-4- Cell transport 1) What is diffusion? Give examples. Movement of particles from higher concentration to lower concentration, no energy needed, 2) What is the diffusion of water? osmosis 3) Differentiate between the three different types of solutions and describe what happens to a cell in each Hypotonic- higher conc. of water outside the cell, waster rushes in, cell swells Isotonic- conc. of water equal inside and out, no net movement Hypertonic- higher conc. of water on the inside of the cell, water rushes out, cell shrinks 4) Describe the different types of proteins that are embedded in the cell membrane and their functions . Transport- move things into and out of cell Receptor- bind to thins on outside of cell membrane and cause a reaction on the inside of the cell Enzymes- speed up chemical reactions Cell surface markers- identify the type of cell 5) Define and give examples of active transport Movement of particles form lower conc. to higher conc., requires energy Sodium/potassium pump Endo and exocytosis 6) Differentiate between endocytosis and exocytosis. Endo – cell membrane envelopes an object, forming a vesicle and brings it into the cell Exo- vesicle inside cell binds to cell membrane ad releases substances outside of the cell BOTH require energy 7) Describe the levels of cellular organization Cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism Chapter 8- Photosynthesis 1) How does energy flow from the sun through living things? Autotrophs capture the sun’s energy and convert It into chemical energy in sugar (glucose) 2) Differentiate between autotrophs and heterotrophs and give examples. An autotroph stores energy from the sun in chemical bonds ( makes its own food), an heterotroph must release energy from food ( cannot make its own food) 3) What are the products and reactants of photosynthesis? 6CO2 + 6H2O -----> C6H12O6 +6O2 (carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight yield glucose and oxygen) 4) Why does chlorophyll appear green? Because it absorbs all other wavelengths of light except green, green light its reflected 5) Label the parts of a chloroplast. Thylakoids, granum, stroma 6) What happens when chlorophyll is struck by sunlight? Electrons get excited and move down the thylakoid membrane 7) What are the steps of the light dependent reactions? Electron transport chain- light is captured, electrons are excited, electrons are replaced by breaking apart a water molecule, oxygen is released into the atmosphere, hydrogen ions diffuse through the ATP synthase and form ATP molecules with each turn 8) What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis? Temperature, sunlight 9) What are some electron carrying molecules involved in photosynthesis? NADP+, ADP Chapter 9- Cellular respiration 1) Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Which yields more energy? Aerobic- with oxygen, anaerobic- without oxygen 2) Describe the structure and breakdown of ATP. ATP contains an adenine, ribose (sugar), and three phosphate groups, when the 3rd phosphate is removed, energy is released, when the 3rd phosphate is added, energy is stored 3) Describe the order of steps in cellular respiration Glycolysis, krebs cycle, electron transport chain 4) Where does cell respiration take place? Glycolysis in the cytoplasm, krebs and ETC in the mitochondria 5) What are some electron carrying molecules used in cell respiration? ADP, NAD+, FADH 6) Give examples of lactic acid and alcoholic fermentation. Lactic acid- muscle cells, dairy products Alcoholic- bread, alcohol 7) How do photosynthesis and cellular respiration form a cycle? They are opposites, The products of one are the reactants of the other, they depend on one another, photo- stores energy, cell resp- releases it Chapter 10 sections 1-3 – Cell cycle, mitosis and regulation 1) Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction (advantages and disadvantages) Sexual- 2 parents, takes longer, fewer offspring, genetic diversity Asexual- 1 parent, quicker, more offspring, no genetic diversity 2) List and describe three types of asexual reproduction Binary fission- copy DNA, split in half, used by bacteria Fragmentation- parent breaks apart and each piece forms new organism Budding- parent grows offspring off side of the body, breaks off. 3) How many chromosomes in a body cell? Human- 46, half form mom and half from dad 4) The correct sequence of the cell cycle. What happens in each phase? G1- cell grows S- Dna is copied G2- prep for division M- two new nuclei form C- cytoplasm splits- 2 new cells are formed 5) How does cancer develop? How can it be treated? A change ( mutation) in DNA causes the wrong protein to be made Uncontrolled cell division results and a tumor forms Radiation, surgery, chemotherapy 6) Identify the phases of mitosis in order (describe and label) Prophase- chromosomes visible, nucleus dissolves Metaphase- chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell Anaphase- chromatids are split apart and move toward opposite ends of the cell Telophase- chromosomes clump together at opposite ends of the cell and two new nuclei form Cytokinesis- cytoplasm splits, two new cells form 7) What are chromatids? Where are they attached? Exact copies of the chromosomes attached at the centromere