* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Gist of It……
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
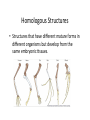
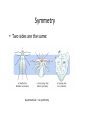
The Gist of It…… EOC Review The Scien6fic Method • Observa6on – State the Problem • Form a Hypothesis – If….then • • • • • Experiment Collect Data Conclusion Publish Your Work Theory Experimental Design Control Group Experimental Group • Control (Placebo) • Independent Variable – variable manipulated by the experimenter – Ex: Caffeine free Coke – Ex: Coke • Dependent Variable – What happens in rela6onship to the independent variable Experimental Design Con6nued How do you control bias? *Blind study/Double blind study Person interested in the results of the study does not do the research!!!! Tools of Science Balance – measures mass Graduated cylinder – volume of a liquid Beaker, flask, etc. – volume of a liquid Microscope – increases the images of an object that is too small to see with the naked eye • Ruler – measures distance • Scien6fic method of measurement? -‐ metric • • • • Photosynthesis/Respira6on reactant -‐-‐-‐-‐> product Photosynthesis: Plants • 6CO2 + 6H2O –light-‐> C6H12O6 +6O2 • Plants use photosynthesis to make food in the chloroplasts Respira9on: Animals • C6H12O6 +6O2 -‐>6CO2+6H2O+ 36 ATP (energy) • Animals use respira6on to make energy (ATP) • Aerobic respira6on – requires oxygen • Anaerobic respira6on – does not require oxygen – leads to fermenta6on Ac6ve/Passive Transport ac9ve passive • Requires energy • Goes against the concentra6on gradient (low to high concentra6on) • May require a pump or gate • Does not require energy • Goes with the concentra6on gradient (high to low concentra6on) • Molecules move through a selec6vely permeable membrane • Looking for equilibrium • Ex: diffusion, osmosis Macromolecules Monomers • • • • Amino acids Triglycerides Glucose (sugars) Nucleo6des Polymers • • • • Proteins Lipids Carbohydrates Nucleic Acids Indicators Macromolecule/Indicator Posi9ve Test • Simple Carb (Glucose)/ Benedicts in a hot water bath • Starch (complex Carb)/ Iodine • Protein/Biuret’s solu6on Turns orange/brown • Lipid/paper bag Turns blue/black Turns violet/purple Bag doesn’t dry, turns translucent Cells • Prokaryote – No nucleus. Includes bacteria. • Eukaryote – Nucleus. Includes plants, animals, etc. Cell Organelles Plant only Animal • Chloroplasts – “kitchen” makes food during photosynthesis • Cell wall (cell plate forms during cytokinesis) • All organelles in the animal cell are present in the plant cell with the excep6on of the cell membrane • • • • • • • • • Mitochondria – “MLGW” powerhouse – makes ATP Golgi Apparatus – “Fedex” packages and distributes proteins ER – “Assembly line” processes and further modifies proteins Lysosomes – “Stomach” breaks up and gets rid of wastes Vacuole – “garage” stores material for later Nucleus – “Brain” controls the cell, contains DNA Ribosomes – “factory” makes proteins Cytoplasm – “soup” organelles and fluid of cell Cell membrane – phospholipid bilayer Cell Division mitosis meiosis • Autosomal cells • Exact copy – 46 chromosomes in each daughter cell • Sex cells • Halves the number of chromosomes – 46 in original cells, 23 in each gamete (sex cell) Dominance Con6nued • Complete dominance – displayed over another trait • Incomplete dominance – traits blend • Co-‐dominant – both traits shown simultaneously DNA Transcrip6on/Transla6on • DNA contains gene6c informa6on • mRNA copies info from DNA and is released into the cytoplasm (Transcrip6on) • tRNA transfers and ahaches the correct amino acid to the forming chain in the ribosome (Transla6on) • rRNA along with other proteins make up the ribosomes that form proteins Extra Stuff • Enzymes – Catalyst in the body – Do not change – Do not get used up – Get recycled – Increase the ac6va6on rate – Decrease ac6va6on energy • Succession – vegeta6on growth – Primary: without soil (ajer volcano, etc) – Secondary: with soil (ajer farming or forest fire) More Extra Stuff • Divergent evolu6on – One organism evolves into many species when adap6ng to different environments • Convergent evolu6on – Unrelated organisms independently evolve similari6es when adap6ng to similar environments Homologous Structures • Structures that have different mature forms in different organisms but develop from the same embryonic 6ssues. Symmetry • Two sides are the same: Asymmetrical – no symmetry