* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 슬라이드 1
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Cracking (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Fischer–Tropsch process wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
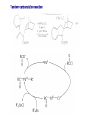
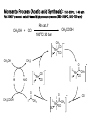
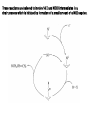
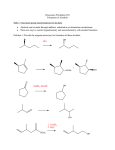
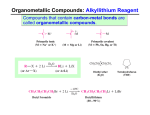
Tandem carbonylation reaction Monsanto Process (Acetic acid Synthesis): 150-200oc, 1-40 atm Ref: BASF process: cobalt-based high pressure process (200-250oC, 500-700 atm) Rh cat./ICH3OH + CO CH3COOH o 180 C/ 30 bar CH 3 CO I Rh CO I I - CH 3I CH 3OH CO Rh CO I I HI H2O O CH 3COOH I - O CH 3 - I CH 3 Rh CO I I O I I CH 3 Rh OC I CO - CO 8.3 Reactions Involving Organonickel Compounds Allylic halides react with nickel carbonyl, Ni(CO)4 to give p-allyl complexes. These reactions are believed to involve Ni(I) and Ni(III) intermediates in a chain process which is initiated by formation of a small amount of a Ni(I) sepcies. This couplig reaction has been used intramolecularly to bring about cyclization of bis-allylic halides and was found useful in the preparation of large rings. Nickel carbonyl is an extremely toxic compound, and a number of other nickel reagents with generally similar reactivity can be used in its place. Mediun sized ring can be formed in intramolecular reaction. The key aspects of the mechanism are (1) the reductive elimination which occurs via a diaryl Ni(III) intermediates and (2) the oxidative addition which involves a Ni(I) species. A soluble bis-phosphine complexes, Ni(dppe)2Cl2, is a particularly effective catalyst. The main distinction between this reaction and Pd-catalyzed cross coupling is that the nickel reaction can be more readily applied to saturated alkyl groups because of a reduced tendency for b-elimination. The synthesis of cyclophane-type structures by use of dihaloarenes and Grignard reagents from a,w-dihalides. When secondary Grignard reagents are used, the coupling product sometimes is derived from the corresponding primary alkyl group. This transformation can occur by reversible formation. Styrene serves to stabilize the active catalytic species, and among the styrene derivatives, m-trifluoromethylstyrene was the best. The main advantage of nickel is that it reacts more readily with arylchlorides and methanesulfonates than does the Pd system. These reactants may be more economical than iodides or triflates in large-scale synthesis. Vinyl phosphates can be used, and these are in some cases more readily obtained and handled than vinyl triflates. 8.4 Reactions Involving Rhodium and Cobalt Hydroformylation The key steps in reaction are addition of hydridorhodium to the double bond of the alkene and migration of the alkyl group to the complexed carbon monoxide. The acylrhodium intermediate is trapped by internal nucleophiles. Fischer-Tropsch Process: reductive conversion of carbon monoxide to alkane by reacting with hydrogen gas. Synthetic hydrocarbon fuels.(1923-1925) In1944, 600,000 ton/yr was produced. Since 1957 South Africa use this method, Sasol Process. Under appropriate conditions, rhodium catalyst can be used for the decarbonylation of aldehyde and acyl chlorides. The use of cobalt for synthetic purpose is quite limited. Vinyl bromides and idodides couple with Grignard reagents in good yields, but a good donor solvent such as NMP or DMPU is required as a cocatalyst. 8.5 Organometallic Compounds with p bonding Among the classes of organic compounds that serve as p ligands are alkene, allyl, dienes, cyclopentadiene anion, and aromatic compounds. The reactivity depends on the following factors a) The number of electrons that can be accommodated by the metal orbitals b) the oxidation level of the metal, c) the electron character of other ligands on the metal Both thermal and photochemical reactions are used. P-allyl complexes of nickel can be prepared either by oxidative addition on Ni(0) or by transmetallation of a Ni(II) salt. Oxidative decomposition Trapping experiments In 1956, Longuet and Orgel propose the complex compound. In 1959, Criegee isolated the complex. One of the best known of the p-organometallic compounds is ferrocene. The molecules behave as an electron-rich aromatic system, and electrophilic substitution reactions occur readily. Reagents that are relatively strong oxidizing agents, such as the halogens, effect oxidation at iron and destroy the compound. Effective Atomic Number: 18 One of the most useful types of p-complexes of aromatic compounds from the synthetic point of view are chromium complexes obtained by heating benzene or other aromatics with Cr(CO)6. The Cr(CO)3 unit is strongly electron-withdrawing and activates the ring to nucleophilic attack. oxidize Existing substituent groups such as CH3, OCH3, and +NMe3 exert a directive effect, often resulting in a major amount of the meta substitution product.