* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kuo: HapMap project
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic studies on Bulgarians wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
HLA A1-B8-DR3-DQ2 wikipedia , lookup
Haplogroup G-M201 wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
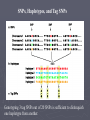
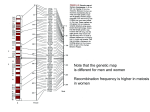
The International Consortium. The International HapMap Project. Nature. 426, 789-796 (2003) The International HapMap Project ► Launched October 29, 2002 ► Major initiative to map human genetic variation based on haplotype patterns. ► Characterize sequence variants, their frequencies, and correlations between them. ► Serve as a key resource for finding genes that affect health, disease, and drug response. Direct Approach: Laborious and Expensive ► Whole genome sequencing of numerous patient samples to identify candidate variations ► Test each variant for correlation with a disease. ► Genotyping 3 million SNPs in 1000 people = 3 billion separate genotyping assays Indirect Approach: Efficient and Comprehensive ► Relatively small set of variants will capture most common variation patterns. ► Linkage Disequilibrium (LD) in SNPs = few haplotypes in many chromosome regions ► A set of sequence variants serve as genetic markers to detect association between a particular genomic region and disease. HapMap ► A few common haplotypes among many chromosome regions account for most of the variation in the human genome. ► Human genome can be divided into 200,000 haplotype blocks. ► Identify 200,000 to 1 million tag SNPs ► Efficient and comprehensive SNPs, Haplotypes, and Tag SNPs Genotyping 3 tag SNPs out of 20 SNPs is sufficient to distinquish one haplotype from another. Haplotype Map: Search for genes on Chromosome 5 Related to Crohn’s Disease Haplotype blocks contain 2-4 flavors of SNP combinations ( orange, purple, etc. ) Dashed lines indicate relationships between blocks Percentages indicate occurrence of each SNP set in patients. DNA Samples and Populations ► Population Sampling: samples chosen from particular populations based on ethnicity and geography. Ancestry N & W European African Japanese Chinese Location United States Ibadan, Nigeria Tokyo, Japan Beijing, China Number of Samples 90 90 ( 30 trios ) 45 ( unrelated ) 45 ( unrelated ) Include a substantial amount of genetic variation Trios and unrelated individuals: local LD patterns. Unrelated DNA samples: identify 99% of haplotypes, frequency of 5% or greater in a population SNP Selection ► ► ► High density of SNPs to adequately describe genetic variation LD and haplotype density varies 100 fold across the genome. Hierarchical strategy will allow regions of the genome with the least LD to be characterized with higher SNP density. Priorities Verified SNPs with available allele frequency and genotyping data Double-hit SNPs seen twice in two different DNA samples SNPs that cause amino acid changes GENOTYPING ► 10 genotyping centers: Japan, UK, Canada, China, US, and Nigeria ► 5 high-throughput genotyping technologies ► Performance criteria: 1. Data produced must be 99.2% complete & 99.5% accurate. 2. All experiments must include samples for internal quality checks. 3. Samples of SNP genotypes from each center re-genotyped by other centers. Various platforms allow for comparisons for accuracy, success rate, throughput, and cost. Complete and reliable data production DATA ANALYSIS ► ► ► ► ► ► ► Analyze LD between markers. Measure proportion of common ancestral chromosomes that have not recombined Sliding window LD profiles LD unit maps Haplotype blocks Meiotic recombination rates Statistical methods, replication studies, and functional analyses of variants – confirm the findings and identify functionally significant SNPs.