* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 Notes- Cell Structure and Function
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
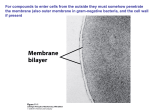
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Chapter 3 Notes- Cell Structure and Function Name________________________ 3.1 A look at Cells 1. Living things may be either _______________________ ( consisting of one cell) or ____________________________( many-celled). Pg. 58 2.Give an example of a unicellular organism. ____________________pg. 58 3.Give an example of a multicellular organism. ___________________pg. 58 4. Look at Figure 3.1. Draw and label the nerve cell, bacterium, Egg cell, and muscle cell. Pg. 58 5. Cells vary greatly in _________________ and shape. A cell’s shape is related to its ___________________. Pg. 58 6. The invention of the ______________________ was one of the most important breakthroughs in biology. Pg. 59 7. Write down the 3 principles of the cell theory: pg. 60 a.__________________________________________________________________ b. __________________________________________________________________ c. __________________________________________________________________ 8. The cell theory emphasizes that all organisms are composed of ______________ the fundamental units of life. The cell theory has provided direction for the work of many biologists and physicians as they study ___________________________ _______________________________________________________________ pg. 60 9. _______________ microscopes can magnify objects such as tiny organisms up to about ________________ times . (pg. 60) 3.2 Basic Cell Structures 10. All cells have these three common features: ___________________, ____________________ and ___________________ (pg. 62) 11. The cell membrane is a thin layer of ____________ and ___________ and separates the cell’s contents from its _____________________. 12. A stack of ________________ membranes is about equal to the thickness of _______________________. (pg.62) 13. The cell membrane functions like a fence with gates, __________________ ___________________________________________________. Pg. 62 14. Molecules are made up of mostly __________________________. Pg. 62 15. A phospholipids is a type of lipid made from _________________, ___________________, and ____________________. Pg. 62 16. The two ends of the phospholipid molecule have different properties in ____________. The ________________ head of the phospholipids is __________________, meaning water-___________. The lipid ___________ of the molecule are _________________, meaning water- ____________.pg. 62 17. Draw and label figure 3.9. 18. The material between the cell membrane and the nucleus is call the __________________. Pg. 63 19. The cytoplasm is a _______________ substance made primarily of _________________ and ___________________________. Pg. 63 20. Various structures called ___________________ or “little organs” are suspended in the cytoplasm. Pg. 63 21. Describe the function of the following: (pgs 64-66) a. Cytoskeleton_____________________________________________________ b. Nucleus _________________________________________________________ c. Chromosomes ____________________________________________________ Read the following statements. If the statement it true, place an X in the box or boxes. Pgs. 64 & 65 22. Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Has a Nucleus Contains DNA The cell type for animal and plant cells. The cell type for bacteria Simple in structure- Do not have organelles More complex- have specialized organelles 23. Explain how cells are like small factories. (Pg. 66) 24. Describe the function of the following organelles(pg. 66); include what it’s job would be as a machine in a factory (pg. 67) a. Ribosomes b. Endoplasmic Reticulum c. Golgi Apparatus d. Mitochondria e. Lysosomes 25. Many cells have unique extensions of their cytoskeleton which are used for movement. ______________ and _________________ are both used for cell movement, but are different in structure and _______________. Pg. 68 3.4 Cell Diversity 26. Look at figure 3.15. (pg. 69) a. List the structures found only in plant cells. b. List the structures found only in animal cells. 27. Describe the function of the following organelles: pgs. 69 and 70 a. Cell wall b. Chloroplasts c. Vacuole 28. Fill in the chart below with a YES or a NO. A comparison of Cells Structure Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Animal Plant Cell Membrane Cell Wall Nucleus Chromosomes Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Mitochondira Chloroplasts Cytoskeleton 3.5 Cells and Their Environment 29. All cells live at least partly in touch with a _______________ solution. In order to live, all cells must ___________________________ and ___________________________________. Pg. 72 30. A _________________________ membrane lets certain molecules pass through and ________________other molecules from crossing. _________ membranes are semi-permeable. Pg. 72 31. Give an example of a molecule that can pass freely through a cell membrane. pg. 72 32. Define the following types of cell transport. Pg. 72 a. Passive transport b. Active transport 33. The most common form of passive transport is ________________. Pg. 72 34. Diffusion is the random movement of ________________ from an area of _____________ concentration (more molecules) to an area of lower concentration (fewer molecules). Pg. 72 35. Look at figure 3.17. Draw the Before and After pictures of the cell. Before After What is different? ______________________________ 36. The rate of diffusion depends on __________________ and the ___________ of the molecules involved. Pg. 72 37. Diffusion always occurs _____________ a gradient. Pg. 72 38. Some molecules diffuse across cell membranes with the help of _____________ _________________. This form of _______________ transport is called __________________ __________________. Pg. 73 39. The diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane is called __________________. Pg. 73 40. Draw figure 3.19 below. How has the concentration of the solute changed in the beaker on the right? 41. Use page 76 and figure 3.22 to help you compare and contrast exocytosis and endocytosis. Exocytosis Endocytosis Define Draw