* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download protein/power point
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
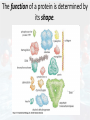
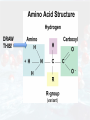
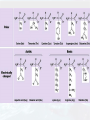
HAPPY TUESDAY Bellwork: Compare and Contrast Carbohydrates vs Lipids Carbohydrates Lipids Five functions of proteins include: • Controlling the rate of reactions (enzymes). • Regulating cell processes (enzymes). • Forming bones and muscles. • Transporting substances into or out of cells. • Helping to fight disease. Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. More than 20 different amino acids are found in nature. The instructions for arranging amino acids into many different proteins is stored in DNA. A protein has four levels of organization. The function of a protein is determined by its shape. DRAW THIS! Now let’s review… The four groups of organic compounds found in living things are: • Carbohydrates • Lipids • Nucleic acids • Proteins Functions: Structure: •Peptide bonds connect the amino acids •Enough amino acids connected together will cause the protein to fold and create a new shape Elements: Controlling the rate of reactions (enzymes). Regulating cell processes (enzymes). Forming bones and muscles. Transporting substances into or out of cells. Helping to fight disease (antibodies). Function is determined by shape! Good to know: •Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N) Protein Monomer: •Amino acid •Examples: Serine (Ser), Proline (Pro) •The R group changes. •The instructions to make proteins is stored in DNA Polymer: •Protein (also called a polypeptide) •Examples: insulin, alcohol dehydrogenase Vocabulary Atom Molecule Reactant Product MacroMacromolecule PolyMonoPolymer Monomer LysisDehydrationSynthesis Hydrolysis Synthesis Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Monosaccharide Polysaccharide Fatty Acid Triglyceride Amino Acid Polypeptide Compare and Contrast Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Proteins. Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins