* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plasma Membrane
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
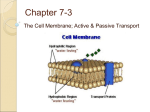
Plasma Membrane Phospholipid • Phospholipid Animations (3) Phospho head – polar Lipid tail nonpolar Phospholipid Bilayer • Hydrophilic heads (water-loving) Hydrophobic tails (water-hating) Fluid Mosaic Model • BBC Education - AS Guru - Biology - Cells - Pathways - Plasma Membranes Proteins in Membrane Cholesterol: add stability to membrane in higher temperatures Carbohydrate Chain Carbohydrate Chain: Used as Identification Markers PROTEIN JOBS: attaches to cytoskeleton PROTEIN JOBS: • Enzymes which are catalytic teams for molecular assembly lines • A Biochemical Pathway (click on animation) • Biochemical Pathway Animation II (CLICKALSO CLICK ON ARROWS) PROTEIN JOBS-Receptors: enable cells to detect chemical messages from other cells PROTEIN JOB: Signal Transduction • Receptor binds to trigger a chain reaction • EXAMPLE ANIMATION (CLICK ON START AND NEXT) MAP Kinase Signal Transduction Animation by Dr. Vic Lemas at BioCreations • Another Signal Transduction Animation Interactive Concepts in Biochemistry Interactive Animations Signal Transduction Diagram Diffusion • Movement of a substance from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration Diffusion • Scientific Method (diffusion animation) Facilitated Diffusion • A protein helps the substance (like an ion) across the membrane Facilitated Transport • Facilitated diffusion involves the use of a protein to facilitate the movement of molecules across the membrane. • Cell Animations (scroll down to Carriermediated passive transport Facilitated transport) Passive Transport • Cell does not need to use energy • Movement of molecules goes “down the gradient” (from high to low concentration) – Diffusion – osmosis – Facilitated diffusion Active Transport • During active transport, cell needs to use energy (ATP) as molecules against a concentration gradient (low concentration to high concentration). – endocytosis – Exocytosis – Pumps (USE ATP) • Cell Animations (scroll down to active transport) Comparing Active and Passive Transport • Shockwave Click here Endocytosis • The process by which a cell engulfs material to bring it into the cell is called endocytosis. A vacuole is formed that contains the material that has been engulfed. Exocytosis • Vesicle fuses with plasma membrane to exit the material outside the cell • (cell pooping) Endocytosis Animation • Endocytosis and Exocytosis Animation • What is the difference between the two? Which brings material in and which brings materials out of the cell? • Endocytosis is in • Exocytosis is out Diffusion: flow from high to low concentration • Also facilitated diffusion (protein channel) Diffusion Things that can pass freely through the plasma membrane • • • • • • • • Hydrophobic molecules (oil soluble) O2 N2 Nonpolar Benzene Small uncharged Polar molecules H2O CO2 Molecules that don’t pass through the phospholipid bilayer easily... • • • • • Large uncharged Glucose Polar molecules Sucrose Ions (charged) H+ , Na+ , HCO3 , K+, Ca+2,Cl- , Mg+2 So what three characteristics of a molecule determine the permeability of the membrane? • Charge • Size • Polarity • However: some molecules which we would think should (or should not) cross the plasma membrane do (or don't) because of the presence of the membrane proteins. Osmosis • Osmosis is the movement of water from a region of high water concentration to a region of lower water concentration through a selectively permeable membrane. • The Cell: Passive Transport Osmosis - Learning - click Solution Vocabulary Solution = solvent + solute Solute- what is being dissolved EX: salt Solvent – what is doing the dissolving EX: water Osmosis • Scientific Method (animation) Hypotonic Solution • Osmosis (click for animation) • A hypotonic solution is one that has less solute (more water). • Cells in hypotonic solution tend to gain water. Isotonic Solution • Osmosis (click for animation) • the concentration of solute is the same on both sides of the membrane (inside the cell and outside). • A cell placed in an isotonic solution neither gains or loses water. Most cells in the body are in an isotonic solution. Drag the bag • Osmosis (predict what will happen) • LabBench (do a little experiment) Hypertonic Solution • Osmosis (click for animation) • A hypertonic solution is one that has a high solute concentration. • Cells in a hypertonic solution will lose water. Plasmolysis • Plant cells placed in a hypertonic solution will undergo plasmolysis, a condition where the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall as the cell shrinks. • The cell wall is rigid and does not shrink. before Osmosis Lab • Use grams on the scale. • Be very careful when carrying (use a spoon) and drying the egg (gently with a paper towel). • Two set-ups per lab table. (If one side breaks, you have a back-up.) • WHEN FINISHED: Clean beakers. Dry off scale and turn off. •Watch the chloroplasts • Plasmolysis of Elodea • Also scroll down for rehydration of elodea Plant Cell Plasmolysis Stiff Cell wall Plasmolysis: Flaccid: Sunken in Normal pressure Cell wall on cell wall Turgid: Lots of pressure on cell wall Can you tell which is the plasmolyzed and which is normal elodea? Compare Plant Cells Plasmolysis • NORMAL CELL water moves toward the area with a higher solute concentration because it has a lower water concentration. water moves from hypotonic to hypertonic solution. Red Blood Cells p. 83 Solutions • If a cell is in a Hypotonic solution, the cell will… • lose water • If a cell is in a Hypertonic solution, the cell will… • gain water Turgor: pressure of water vacuole on the cell wall of a plant Active Transport • Active Transport Animation • Cell needs energy to move particles “against the gradient” from low to high concentration Active Transport Active Transport • "pumps" materials across the membrane against the concentration gradient. i.e. ,from low concentration to high concentration (therefore it requires energy). Endocytosis • Endocytosis: Large materials transported into the cell. • Endocytosis includes three slightly different processes: – Phagocytosis – Pinocytosis – Receptor-mediated Endocytosis • Endocytosis - "to enter the cell" • Phagocytosis - large particles - membrane "reaches out" - phago = eat" • Pinocytosis - solutes in fluids - membrane folds in to form a pouch known as a vesicle. - pino = drinking" • Receptor mediated endocytosis - receptors on the membrane attach to large molecules like hormones and folds them inside. Phagocytosis • Animations: • Phagocytosis Engulfing large particles “Cell eating” • Phagocytosis | Flash simulation, Animation, Illustration, Picture, Diagram eduMedia Pinocytosis • “Cell drinking” • Engulfing small liquid droplets Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis • Receptor Mediated Endocytosis • Specialized receptor that just fits a specific substance • EX: LDL • Hormones • insulin Receptor Mediated Endocytosis Exocytosis • Material (wastes etc.) are expelled from the cell • • Table 8.2: Five processes by which substances move across cell membranes. Simple Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Particle Movement High to low High to low Active Transport Low to high Exocytosis Intracellularl to extracellular Endocytosis Extracellular to intracellular • Protein Carrier Energy Required No No Yes No Yes Yes No, occurs by fusion of vesicles with cell membrane. No, occurs by involution of cell membrane. Exocytosis