* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes 1 Introduction to Chapter 5
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
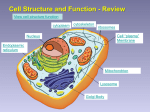
Notes 1 Introduction to Chapter 5 Page 97 With your table: 1) Watch this video. 2) Answer these questions: a) What is this organism? b) What is the organism doing? c) You know a little about the structure of cell membranes. How is this possible? Standards: CLE 3210.1.5 - Compare different models to explain the movement of materials into and out of the cell. SPI 3210.1.8 - Compare active and passive transport. RLE 2010.2.1 - Recognize the importance of homeostasis as a survival mechanism. Homeostasis • Define homeostasis: a relatively stable state of equilibrium or a tendency toward such a state • Macro example: • Micro example: We maintain a stable body temperature. Cells use the cell membrane to regulate what comes in and out of the cell to keep steady levels of nutrients, water and other substances. Cell Membrane Transport • Two main types of cell transport: o Passive: the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy. o Active: the movement of chemical substances, usually across a cell membrane that requires the use of energy. Cell Energy 1. Energy for the cell is made in the: Mitochondria 2. Energy for the cell is made from: Glucose (simple sugar) 3. The energy molecule used by the cell is: ATP (adenosine triphosphate) Review Homeostasis: a relatively stable state of equilibrium or a tendency toward such a state Two types of Cell Membrane Transport: Passive - uses no energy; Active - uses energy Energy molecule: ATP - made from glucose in the mitochondria is used during active transport.