* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Active transport - CHS Science Department Mrs. Davis
Survey
Document related concepts
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
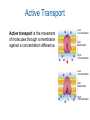
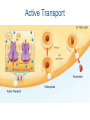
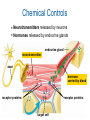
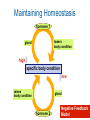
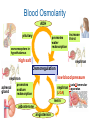
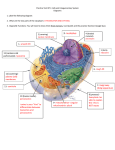
Active Transport & Homeostasis Life Science: Molecular Membrane Proteins Transporters are transmembrane proteins that use energy to move molecules across a membrane. Active Transport Active transport is the movement of molecules through a membrane against a concentration difference. Low Concentration Cell Membrane High Concentration Low Concentration Cell Membrane High Concentration Transmembrane Pumps Protein pumps use energy to move molecules such as calcium, potassium, and sodium ions across the membrane against a concentration gradient. – sodium-potassium pump • pumps sodium out • pumps potassium in Active Transport Active Transport Larger molecules can be transported by movements of the cell membrane known as bulk transport. – Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane. • phagocytosis - cell eating • pinocytosis - cell drinking – Exocytosis is a process of releasing large amounts of materials from the cell. Active Transport Homeostasis • Homeostasis means maintaining a constant internal environment. • Cells need to maintain a narrow range of conditions to stay alive. – – – – – temperature pH salinity minerals glucose Hypothalamus • Hypothalamus = master nerve control center ➡ receives information about internal conditions from nervous system ➡ releases hormones to maintain homeostasis • Pituitary gland = master endocrine gland ➡ secretes broad range of hormones to regulate other glands hypothalamus in the body pituitary Chemical Controls Neurotransmitters released by neurons ➡ Hormones released by endocrine glands ➡ endocrine gland neurotransmitter axon hormone carried by blood receptor proteins receptor proteins target cell Feedback • There are two ways to maintain homeostasis – Positive feedback – Negative feedback Maintaining Homeostasis hormone 1 lowers body condition gland high specific body condition low raises body condition gland hormone 2 Negative Feedback Model Blood Osmolarity ADH pituitary promotes water reabsorption osmoreceptors in hypothalamus high salt increase thirst nephron Osmoregulation low blood pressure nephron adrenal gland promotes sodium reabsorption nephron (JGA) renin aldosterone angiotensin JuxtaGlomerular Apparatus