* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are some types of living things??? - science-doaa
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
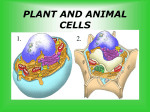
What are some types of living things??? objectives • Classify things into living and nonliving things. • Compare and contrast between living and nonliving things(give example ). • Recognize the needs of living things. • Identify the meaning of organism. • Identify the meaning and types of the cell. • Identify the main parts of the plant cell and its function. • Identify the main parts of the animal cell and its function. • recognize methods to observe living things. The importance of animals homes. • Read the fast fact p. 50 • Where does a seal live? • What might a frog use as a home? • Why do animals live where they do? • What do shelters provide for the living things? Living and non-living • Living things: any thing needs food, water, and air. • Nonliving things: : any thing dose NOT needs food, water, and air. • Once living things are the things that were living after that become nonliving. • Any living thing is an organism. • What is the difference between the cat and plant???(both are living things). • living things reproduce: it makes more of its kids.( cat: kittens – plants: seeds ). • Living things react to changes around them. ( cat run away ). • Living things need energy to grow and move. • People and animals get energy from food, but plants get energy from the sun. Living and nonliving things • Living things • A living thing can reproduce. • It uses energy to grow. Plants use the energy from the sun to make food. • They react to changes in the environment. (examples) Any living thing is an organism • Nonliving things • They can’t reproduce • Don’t grow or change • Don’t react to changes in the environment. From what this wall is made of? Types of cells 15 • Animal cell • Plant cell Nucleus Cytoplasm Vacuole Cell Membrane Chloroplast Cell Wall cells • All living things made up of parts( face- hand- leg…), and these parts made up of a small parts called cells. • Cells are a tiny building block. • it is the smallest unit of a living thing. • Most cells can not been seen without a microscope. • Plant cells can be different in shape and size, but they have the same parts. • Are some cells more important than other cells? explain. • Each cell in an organism has its own job; like in plant: leaf, roots, and stem. • All the cells in an organism work with together to help organism survive. Parts of plant cells • Plant cell 1. Cell wall 2. Cell membrane 3. Nucleus 4. Cytoplasm 5. Vacuoles 6. Chloroplasts Functions of the parts • Cell wall: it gives the cell its shape. • Cell membrane: it keeps not needed substances out of the cell. It protects the parts inside the cell. • Cytoplasm: keeps cell parts in place. • Chloroplasts: make food to enable a plant to get energy it needs to stay a live. • Nucleus: tells the rest of the cell parts how to do their jobs, just like the brain in human. • Vacuole: a storage location in cells Animal cell • Animals made up from cells. • Each cell has its own job: – Skin cells protect it from the outside. – Muscles cells join together to make muscle for moving. Parts of the animal cells • Animals cells have 4 main parts: – Cell membrane – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – vacuole Differences between animal and plant cells vacuole Observing living things • We can see some living thing easily by our eyes. • Some living things are too small that we need to use microscope to see them. • We can use hand lens (magnifier) and binoculars in observing living things.