* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Concepts of Genetics
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
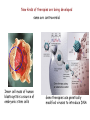
Welcome to BI 142 The Genetic Century Instructor: Dr. Clare O’Connor Office hours: F 3-5 in Higgins 478 or by appointment Teaching Assistant: Karen Zhu Course syllabus is posted on Canvas Links to course readings are incorporated into calendar: Scientific American articles Concepts of Genetics (open access biology text) Scitable (Nature Education Site) U. Utah Genetics Learning Center Others.... Lecture capture can be accessed through the Echo Center Note - the syllabus is dynamic and will undergo changes during the semester - Access it often!! Course Grading Midterm exams (3 -100 points each) 300 Final exam 200 Online quizzes (10 points each) 50 (normalized) Clicker points (present for 75% questions) 50 (normalized) Class assignments 50 (normalized) Group presentations 100 (Genes in the news) “Bump” points based on class participation (cold calls) Register your i-clicker on Canvas Some clicker practice! Quiz 1 – course concepts you receive 10 points for completing it before the next class What are some of the issues that we will address in this class? Our understanding of ourselves: Do our genes determine our destiny? Identical twins have the same genes Phenotypes result from genes and environmental factors Human diversity: Our unique genetic identity Our genetic relatedness Medicine becomes personalized A new, molecular understanding of disease Metabolic diseases Marfan syndrome Huntington’s Disease Sickle cell disease The foods we eat How did our foods originate? Are genetically modified foods a good idea? Flavr Savr tomatoes Monsters??? Golden rice Our understanding of life’s history Credit: nbii.gov This is not the first genetic century Civilization depended on man’s (unwitting) manipulation of genetics Wheat, peas, olives Corn, beans, squash Southwestern Asia 8500 BC Mesoamerica by 3500 BC Rice, millet China 7000 BC Civilizations depend on cereal crops Potatoes Andes by 3500 BC In less than 100 years after Mendel discovered the basic principles of inheritance (1865), ….the first “molecular disease”, sickle cell anemia, was identified by Linus Pauling (1949) ….the structure of DNA was described as a double helix by Watson and Crick (1953) Genome: the complete genetic information of an organism The 21st century began with the draft sequence of the human genome Begun in 1990 Draft sequence - 2001 Completed - 2003 (exactly 50 years after the structure of DNA was solved) A human genome can now be sequenced for several thousand dollars New kinds of therapies are being developed some are controversial Inner cell mass of human blastocysts is a source of embryonic stem cells Gene therapies use genetically modified viruses to introduce DNA Genetic engineering continues to advance Cloned organisms Genetically modified organisms GloFish Drugs are produced by organisms grown in bioreactors Genome sequencing costs have dropped significantly: The $1000 genome may not be far off One view: A deterministic future based on genetics? 1997