* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
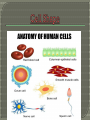
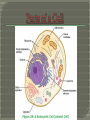
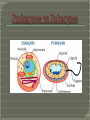
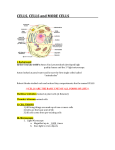
The History of Cell Biology Introduction to Cells Cell Organelles and Features Unique Features of Plant Cells The cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the process of life. In complex organisms it is the basis of the organizational structure. Cells > Tissues > Organs > Organ System > Organism Robert Hooke- was a scientist in the 17 th century who contributed in the fields of biology, physics and astronomy. Studied objects in nature using a light microscope. Looked at a thin slice of cork from a cork oak tree. It was made up of many tiny little boxes which reminded him of cubicles or cells where monks live. Anton van Leeuwenhoek- a Dutch Trader and a lens grinder. Was able to make microscopes that had 10 x the magnification of Hooke’s microscope. The first person to observe living cells. Looked at alga underneath a microscope. Three Essential Parts • All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. • Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells. The Cell Theory and its three parts. Robert Hooke and his contributions. Anton van Leeuwenhoek and his contributions. The light microscope and the role it played. What do you know about cells? http://www.softschools.com/science/mic roscope_parts/ https://www.brainpop.com/games/virtua llabsusingthemicroscope/ http://ideastream.pbslearningmedia.org /resource/f4f6097a-807f-4488-b8740bae0d8446c8/microscope-activity/en/ Cell Diversity Basic Parts of a Cell Two Basic Types of Cells Cellular Organization Cell Shape-different cell shapes reflect the different functions of cells. Cell Size-Some cells can be 2 m long while some cells are only 10 to 50 micrometers. Plasma membrane-covers a cell’s surface and acts as a barrier between the inside and the outside of a cell. Cytoplasm-the region of the cell that is within the plasma membrane and that includes the fluid, the cytoskeleton, and all of the organelles except the nucleus. Control Center-area of the cell that carries DNA that codes for the cells actions. Prokaryotes-organisms that lack a membrane bound nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Eukaryotes-organisms made up of one or more cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Colonies-a collection of genetically identical cells that live together in a connected group. (Not Multicellular) True Multicellularity-A group of similar cells working together to carry out a specific function. The three basic parts of a cell. Two types of cells. Colonies vs. True Multicellularity http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/healt h/anatomy/cell/index.htm https://www.centreofthecell.org/learnplay/games/ http://www.biomanbio.com/GamesandL abs/Cellgames/Cells.html http://www.cellsalive.com/ http://sepuplhs.org/high/sgi/teachers/c ell_sim.html