* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Flat file for auto loading into the CBO 1.0 version. Individual sections
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
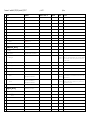
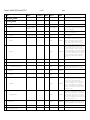
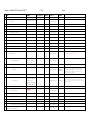
Document1 modified 2/25/2011 printed 5/5/2017 p. 1 of 11 j sluka Flat file for auto loading into the CBO 1.0 version. Individual sections delimited by Heading1 and by new BFO classes Use <ctrl><tab> to insert the hard tabs needed for Protege4 http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ontology-lookup/ http://bioportal.bioontology.org/ GO, CL and FMA are all OWLs, PRO and CellO are OBOs BFO uses “Quality”, OPB uses “Property” Class 1 Comments External child of BFO:independent_continuant: material_entity:object ExtRefs Definition physical_entity_type 2 corpuscular_entity Not divisible without fundamental change in character 3 continuous_entity Divisible without fundamental change in character (“portionOf”_ 4 Issues physical_bounded_object BFO:independent_continuant: material_entity:object Object with physical extents. 5 discrete_physical_object Physical object that is not composed of physical subobjects 6 aggregate_physical_object Physical object that is composed of physical sub-objects 7 physical_object_quality 8 energy 9 geometrical_properties 10 volume 11 shape 12 13 BFO:...:quality BFO uses “Quality”, OPB uses “Property” Quality and characteristics of physical objects, e.g., location, volume, energy etc. BFO uses “Quality”, OPB uses “Property” body anisotropy directed 14 polarity 15 undirected 16 elongation 17 18 isotropy 19 protrusions 20 position 21 center_of_volume 22 cnter_of_mass 23 orientation a mathematical point Document1 modified 2/25/2011 printed 5/5/2017 Class Comments 24 surface_area 25 location 26 extent 27 discrete 29 dimensionality 30 1d 31 2d 32 fractal 33 3d 34 texture 35 uniformity 36 pattern 37 gradient 38 39 40 kinetic_properties mass mechanical_properties Deprecated, use OPB Deprecated, use OPB Deprecated, use OPB 41 yieldingthreshold Deprecated, use OPB 42 youngsmodulus Deprecated, use OPB 43 pressure Deprecated, use OPB 44 adhesiveproperties Deprecated, use OPB 45 tension Deprecated, use OPB 46 stiffness Deprecated, use OPB 47 poissonratio Deprecated, use OPB 48 chemicalproperties Deprecated, use OPB 49 localization Deprecated, use OPB 50 affinity Deprecated, use OPB 51 pattern Deprecated, use OPB 52 53 54 55 gradient density electricalproperties charge External child of j sluka Issues ExtRefs Definition Surface area in three dimensions, length in two dimensions. continuous 28 p. 2 of 11 Deprecated, use OPB Deprecated, use OPB Deprecated, use OPB Deprecated, use OPB Document1 modified 2/25/2011 printed 5/5/2017 Class Comments 56 voltage Deprecated, use OPB 57 current Deprecated, use OPB 58 capacity Deprecated, use OPB 59 resistance Deprecated, use OPB 60 conductivity Deprecated, use OPB 61 gravity Deprecated, use OPB 62 movementfield Deprecated, use OPB 63 statisticalproperties Deprecated, use OPB 64 random p. 3 of 11 External child of j sluka Issues ExtRefs Definition Deprecated, use OPB 65 66 geometrical_entity 67 boundary 68 cell_regions 69 basal_part 70 apical_part 71 lateral_part 72 medial_part 73 Sub-entities Group with other cell parts? GO: The region of a cell situated near the base. For GO:0045178, example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the basal surface FMA:72558 rests on the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue. organismal_regions 74 dorsal posterior: but humans vs. quadripeds are different Dorsal is a geometric modifier describing parts of an EFO_0001656 organism relating to or situated near or on the back. For , FMA:74535 example dorsal fin. 75 ventral anterior: but humans vs. quadripeds are different EFO: Ventral is a geometric modifier describing parts EFO_0001662 pertaining to the front or anterior of any structure for example ventral striatum. 76 temporal_entity 77 material_type 78 fluid 79 solute 80 solid 81 gel 82 Sub-entities, use OPB Document1 modified 2/25/2011 printed 5/5/2017 Class Comments p. 4 of 11 External child of 83 system BFO:independent_continuant: material_entity:object 84 cell BFO:independent_continuant: material_entity:object 85 molecule 86 extracellular_matrix j sluka Issues ExtRefs The “universe” described by the model. GO:0005623, GO:The basic structural and functional unit of all CL:0000000, organisms. Includes at least the plasma membrane and the FMA:68646 cytosol. GO:0031012, FMA:9672 87 interstitial_matrix GO:0005614 88 basement_lamina GO:0005605 89 90 91 molecular_field medium cell_part 92 nucleus 93 cell_border 94 cell_membrane 95 cell_wall 96 97 cytoplasm cell_membrane_part 98 membrane_receptor 99 adhesion_molecule 100 tight_junction 101 gap_junction 102 pump 103 ion_channel 104 105 Definition cell_membrane_local_structu re filopodium Depends on cell, only cell border and cytosol required BFO:dependent_continuant: specifically_dependent_contin uant FMA:61764, Any constituent part of a cell. GO:The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, GO:0005634, such as protein complexes. FMA: Cell substance which fills FMA:63840 the cell compartment between the plasma membrane and the nuclear membrane (for eukaryotes). Necisary and sufficient condition for a cell, with cytosol. In plants the cell wall is considered part of the ECM Necisary and sufficient condition for a cell, with cell_border. Depends on cell_membrane Depends on cell_membrane FMA: Cell component which consists of cytosol and cytoplasmic organelles. Membrane v. border? GO:0044459, GO: plasma membrane part; Any constituent part of the plasma membrane, the membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. FMA:67214 FMA: Cell adhesion molecule Membrane v. border? A thin, stiff protrusion extended by the leading edge of a motile cell such as a crawling fibroblast or amoeba, or an axonal growth cone. Document1 modified 2/25/2011 printed 5/5/2017 Class p. 5 of 11 Comments j sluka External child of Issues ExtRefs Definition 106 brush_border GO: Dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of epithelial cells in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell. 107 pseudopodium GO: A temporary protrusion or retractile process of a cell, associated with flowing movements of the protoplasm, and serving for locomotion and feeding. 108 cell_type 109 prokaryote 110 eukaryote 111 anuclear 112 virus Cell_type by broad phyla Cell without nuclei, e.g., platelets and erythrocytes. Not to be confused with non-nuclear prokaryotic cells. Cell without nuclei, e.g., platelets and erythrocytes. Not to be confused with non-nuclear prokaryotic cells. MISSING Characteristics: shape, type (CL, ChEBI, GO…) … terms Process_tree From BFO we have “fiat_process_part” for processes without well-defined beginnings and endings (e.g., motility) and “process” which have a specific time referent, like cell division or well defined beginning and ending time. For now everything put under “process”. 113 114 Class Comments BFO Child of fundamental_physical_process Generic terms. Cell has its own subset. BFO:occurrent: processual_entity: process Issues Links to ExtRefs Definition occurrent: processual_entity: process movement 115 translation fiat_process_part 116 rotation fiat_process_part 117 diffusion fiat_process_part 118 shape_change fiat_process_part 119 volume_change fiat_process_part 120 expansion fiat_process_part 121 contraction fiat_process_part 122 creation 123 deletion 124 phenotypic_change 125 barrier_crossing process process Includes molecular changes such as ionization process process Includes molecular changes such as ionization Document1 modified 2/25/2011 printed 5/5/2017 Class 126 127 128 Comments p. 6 of 11 BFO Child of j sluka Issues Links to ExtRefs structural_process cellular_process Prodcess does not result in a change in the identity of the Object, but the Object does change in DATA structure existential_cellular_processes 129 cell_growth 130 cell_division 131 fission 132 mitosis Volumetric, includes contraction For example, bacteria. fiat_process_part FMA: The process in which a cell irreversibly increases in size over time by accretion and biosynthetic production of matter similar to that already present. process GO: The process resulting in the physical partitioning and separation of a cell into daughter cells. process Bacterial cell division. process 133 meiosis process 134 cell_division_symmetry process GO:0007067, GO: A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell divides; the process involves condensation of chromosomal DNA into a highly compacted form. Canonically, mitosis produces two daughter nuclei whose chromosome complement is identical to that of the mother cell. GO:0007126, GO: A cell cycle process comprising the steps by which a cell progresses through the nuclear division phase of a meiotic cell cycle, the specialized nuclear and cell division in which a single diploid cell undergoes two nuclear divisions following a single round of DNA replication in order to produce four daughter cells that contain half the number of chromosomes as the diploid cell. Meiotic division occurs during the formation of gametes from diploid organisms and at the beginning of haplophase in those organisms that alternate between diploid and haploid generations. GO: The asymmetric division of cells to produce two daughter cells with different developmental potentials. It is of fundamental significance for the generation of cell diversity. 135 symmetric_cell_division process 136 asymmetric_cell_division process GO:0008356, process GO:0008219, 137 138 139 140 cell_death necrosis apoptosis autophagic_death Catch all for cell death. process GO:0006915, GO: A form of programmed cell death that begins when a cell receives internal or external signals that trigger the activity of proteolytic caspases, proceeds through a series of characteristic stages typically including rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), and plasma membrane blebbing (but maintenance of its integrity until the final stages of the process), and ends with the death of the cell. process GO:0048102, GO: A form of programmed cell death that is accompanied by macroautophagy, which is characterized by the sequestration of cytoplasmic material within autophagosomes for bulk degradation by lysosomes. Autophagic cell death is characterized by lack of chromatin condensation, massive vacuolization of the cytoplasm, and accumulation of (double-membraned) autophagic vacuoles, with little or no uptake by phagocytic cells. GO:0000768, GO: The formation of a syncytium, a mass of cytoplasm containing several nuclei enclosed within a single plasma membrane, by the fusion of the plasma membranes of two or more individual cells. process 141 cell_fusion process 142 cell_differentiation process 143 Definition cell_environment_process Document1 modified 2/25/2011 printed 5/5/2017 Class 144 145 146 147 Comments p. 7 of 11 BFO Child of j sluka Issues Links to cell_import Via endocytosis, pores etc. fiat_process_part cell_export exocytosis fiat_process_part cell_contact cell-cell_contact fiat_process_part 149 cell-noncell_contact fiat_process_part 150 cell_basement_lamina_contact fiat_process_part 151 cell_interstitial_matrix _contact fiat_process_part cellular_property_process 153 cellular_mechanical_process 154 cellular_kinetic_process 155 geometrical_cellular_process 156 cell_displacement 158 cell_advection 159 chemotaxis 160 haptotaxis 162 fiat_process_part incompatable with GO:0006928 “cell movement” cell_movement 157 161 cell_motility Change in location of center_of_volume or center_of_mass fiat_process_part fiat_process_part fiat_process_part GO:0006935, GO:0060326 GO: The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). GO:0048870, GO: Any process involved in the controlled self-propelled movement of a cell that results in translocation of the cell from one place to another. fiat_process_part Energy consuming random cell movement. Contrast with chemotaxis, haptotaxis which are directional. cell_rotation fiat_process_part fiat_process_part Deprecated. See cell_growth. cell_volume_change 164 cell_shape_change fiat_process_part 165 cell_orientation_change fiat_process_part 166 cell_adhesion fiat_process_part fiat_process_part 167 cell-cell_adhesion fiat_process_part 168 cell-extracellular_matrix_adhesion fiat_process_part cellinterstitial_matrix_adhesion incompatable with GO:0006928 “cell movement” fiat_process_part 163 169 Definition fiat_process_part 148 152 ExtRefs cell-related_transport fiat_process_part Document1 modified 2/25/2011 printed 5/5/2017 Class 171 172 173 174 Comments cell-basement_membrane_adhesion 170 BFO Child of j sluka Issues Links to fiat_process_part cellular_electrical_process cellular_chemical_process cell-cell_process extracellular_matrix_process 175 interstitual_matrix_process 176 basement_lamina_process 177 molecule_process used to be small_molecule_process 178 transport Catch all class. Cell has its own set. 179 p. 8 of 11 interentity_transport process process 180 import process 181 export process 182 183 intraentity_transport molecular_targeting process ExtRefs Definition Document1 modified 2/25/2011 printed 5/5/2017 p. 9 of 11 j sluka CBO Relations Relation links isA OBO-RO:is_A has_quality BFO:inheres_in? OPB:hasProperty? Func Sym Inv Trans ASym Refl Irrefl Func X OWL markup Definition X quality_of quality_of has_part Domain Range Inverse† “cell” hasQuality “volume”, “point” hasQuality “location” has_quality OBO-RO X has_proper_part OBO-RO X has_integral_part OBO-RO X part_of OBO-RO X proper_part_of OBO-RO X integral_part_of OBO-RO X contained_in OBO-RO contains contains OBO-RO contained_in located_in OBO-RO X X location_of location_of OBO-RO X X located_in instance_of OBO-RO CBO model_of † Inverse may be different between classes versus instances. X part_of proper_part_of has_part with the additional restriction that C<>Ci X integral_part_of The defining part of C. “Cell” has_Integral_Part “cell_membrane”. X has_part has_proper_part X has_integral_part Difference between contains and located? Document1 modified 2/25/2011 printed 5/5/2017 p. 10 of 11 j sluka OWL Properties represent relationships. There are two main types of properties, Object properties and Datatype properties. Object properties are relationships between two individuals. Object properties link an individual to an individual. OWL also has a third type of property – Annotation properties. Annotation properties can be used to add information (metadata — data about data) to classes, individuals and object/datatype properties. Figure 4.12 depicts an example of each type of property. CBO dataProperty dataProperty hasFloatValue hasIntValue hasUnit Functional Domains Equivalent Super Disjoint Ranges (intersections) Properties Properties Properties OWL markup Definition X X X CBO objectProperty are relationships between two individuals objectProperty hasLocation hasVolume hasEnergy Func Inv Func Trans Sym ASym Refl Irrefl Domains Ranges (intersections) (intersections) Equivalent Super Inverse Disjoint Property Object Properties Properties Properties Chains Properties OWL markup X X X http://www.berkeleybop.org/ontologies/owl/PATO for units and some shapes? http://forge.morfeo-project.org/wiki_en/index.php/Units_of_measurement_ontology for a discussion of the problem of assigning values and units. :weight a owl:DatatypeProperty ; rdfs:label "Weight" . :weightInKilograms rdfs:subPropertyOf :weight ; rdfs:label "Weight measured in Kilograms" ; Definition Document1 modified 2/25/2011 printed 5/5/2017 p. 11 of 11 j sluka :measuredIn ucum:kilograms . :weightInPounds rdfs:subPropertyOf :weight ; rdfs:label "Weight measured in Pounds" ; :measuredIn ucum:pounds . CBO annotationProperties OWL also has a third type of property – Annotation properties. Annotation properties can be used to add information (metadata — data about data) to classes, individuals and object/datatype properties. See http://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-primer/ ? DC:http://dublincore.org/documents/dces/ (Dublin Core) RDFS:http://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-schema/ annotationProperties description creator Type Defined In ^^PlainLiteral DC DC DC:description DC:creator date ^^Date ? DC DC:date comment ^^PlainLiteral RDFS rdfs:comment discussion label xref versionInfo ^^PlainLiteral RDFS rdfs:label OWL owl:versionInfo DC DC:source source ^^PlainLiteral ^^PlainLiteral Definition An account of the resource. Description may include but is not limited to: an abstract, a table of contents, a graphical representation, or a free-text account of the resource. An entity primarily responsible for making the resource. A point or period of time associated with an event in the lifecycle of the resource. Date may be used to express temporal information at any level of granularity. Recommended best practice is to use an encoding scheme, such as the W3CDTF profile of ISO 8601 [W3CDTF]. Used to provide a human-readable description of a resource. A textual comment helps clarify the meaning of RDF classes and properties. Such in-line documentation complements the use of both formal techniques (Ontology and rule languages) and informal (prose documentation, examples, test cases). A variety of documentation forms can be combined to indicate the intended meaning of the classes and properties described in an RDF vocabulary. Since RDF vocabularies are expressed as RDF graphs, vocabularies defined in other namespaces may be used to provide richer documentation. Used to provide a human-readable version of a resource's name. A related resource from which the described resource is derived. The described resource may be derived from the related resource in whole or in part. Recommended best practice is to identify the related resource by means of a string conforming to a formal identification system. OWL markup