* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH 7 Exam - Deer Creek Schools
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
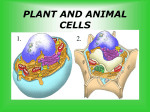
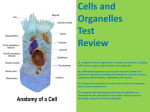
CH 7 Exam: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM! 1. Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory? a. Cells are the basic units of life c. Very few cells reproduce b. All living things are made of cells d. All cells are produced by existing cells 2. Prokaryotes lack a. Cytoplasm b. A cell membrane c. A nucleus d. Genetic material 3. Which of the following contain a nucleus? a. Prokaryotes c. Eukaryotes b. Bacteria d. Organelles 4. Which of the following organisms are prokaryotes? a. Plants c. Bacteria b. Animals d. All of the above 5. Which of the following is a function of the nucleus? a. Stores DNA c. Contains the information needed to make protein b. Controls most of the cell’s processes d. All of the above 6. Which organelle converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use? a. Chloroplast c. Endoplasmic reticulum b. Golgi apparatus d. Mitochondria 7. Which organelles help provide cells with energy? a. mitochondria and chloroplasts c. smooth endoplasmic reticulum b. rough endoplasmic reticulum d. Golgi apparatus and ribosomes 8. Which organelle would you expect to find in plant cells but NOT animal cells? a. Mitochondria c. Chloroplasts b. Ribosome d. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum 9. Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton? a. Helps a cell keep its shape c. Surrounds the cell b. Contains DNA d. Helps make proteins 10. The main function of the cell wall is to a. Support and protect the cell c. Direct the activities of the cell b. Store DNA d. Help the cell move 11. Unlike the cell membrane, the cell wall is a. Found in all organisms c. A flexible barrier b. Composed of a lipid bilayer d. Usually made of tough fibers 12. Which of the following is a function of the cell membrane? a. Breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins from foods b. Stores water, salt, proteins, and carbohydrates c. Keeps the cell wall in place d. Regulates which materials enter and leave the cell 13. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a. an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration b. an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration c. an area of equilibrium to an area of high concentration d. all of the above 14. When the concentration of molecules on both sides of a membrane is the same, the molecules will a. move across the membrane to the outside of the cell b. stop moving across the membrane c. move across the membrane in both directions d. move across the membrane to the inside of the cell 15. Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? a. Diffusion c. Facilitated diffusion b. Osmosis d. Active transport 16. The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called a. Osmotic pressure c. Facilitated diffusion b. Osmosis d. Active transport 17. Which term refers to cells having different jobs in an organism? a. Multicellular c. Levels of organization b. Cell specialization d. Unicellular 18. All of the following are examples of cell specialization EXCEPT a. pancreatic cell that produces protein-digesting enzymes b. muscles cells that control movement of materials in the body c. a prokaryotic cell that carries out photosynthesis d. a red blood cell that carries oxygen 19. The cells of multicellular organisms are a. smaller than those of unicellular organisms b. simpler than those of unicellular organisms c. specialized to perform different tasks d. not dependent on one another 20. Which of the following is an example of an organ? a. Heart c. digestive system b. epithelial tissue d. nerve cell 21. All of the following are types of tissues EXCEPT a. muscle c. digestive b. connective d. nerve 22. A group of similar cells that perform a particular function in called a (an) a. organ c. tissue b. organ system d. division of labor 23. Which of the following is an organ of the digestive system? a. Stomach c. muscle cell b. nerve tissue d. epithelial tissue 24. An organ system is a group of organs that a. are made up of similar cells b. are made up of similar tissues c. work together to perform a specific function d. work together to perform all the functions in a multicellular organism 25. Which list represents the levels of organization in a multicellular organism from the simplest level to the most complex level? a. cell, tissue, organ system c. tissue, organ, organ system b. organ system, organ, tissue, cell d. cell, tissue, organ, organ system 26. Unlike smooth endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum has _____________ attached to it. 27. According to the cell theory, all cells come from existing ____________________. 28. Molecules tend to move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated. This process is called ________________________. 29. Mitochondria produce energy that cells can use. This energy is called ______. 30. Ribosomes produce _________________. The Cell Solution Outside Of Cell Use the figure to below to answer the remaining questions. 31. % water inside the cell= _________________ 10% Salt 32. % water outside the cell= ________________ 33. Is the solution outside of the cell hypertonic, isotonic, or hypotonic? _____________ 34. Is the water moving in or out of the cell? ______________ 35. Will the cell shrink, swell, or experience no osmotic pressure? _____________ 5% Salt