* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anaerobic Respiration
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
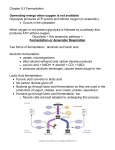
ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION Aida Rogonich, Cristina Botello, Jacqueline Enriquez, Sarah Wolberg, Takira ALCOHOL FERMENTATION: STEP ONE Glycolysis is the breaking of a carbohydrate into two pyruvates Occurs in the cytoplasm of cells No oxygen needed. GLYCOLYSIS: PART ONE 2 PGAL’s (Phosphoglyceraldehyde - 3Carbon molecules) are formed from the breaking down of glucose (6C) Two ATP's are required GLYCOLYSIS: PART TWO 2 pyruvates are created from 2 PGAL's (3C) Producing 4 ATP's and 2 NADH's Net production = 2ATP’s and 3 NADH’s 2ND STEP WHERE DOES IT OCCUR? IN THE CYTOSOL OF YEAST! No oxygen is used 2 Acetaldehyde is reduced by NADH to ethanol Regenerating supply of NAD+ Carbon dioxide may be realeased Glycolysis continues 2ND STEP CONT. When the first step occurs and 2 acetaldehyde is formed, 2 CO₂ is released Then acetaldehyde accepts hydrogen and electrons from the 2 NADH formed through Glycolysis With the combining of e-, H+, and 2 acetaldehyde, 2 NAD+ is regenerated and 2ethanol is created ALCOHOLIC FERMENTATION: Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pі 2 ethanol + 2 CO₂ + 2 ATP + 2 H₂O LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION: Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2 lactate + ATP + 2 H₂O OR C₆H₁₂O₆ 2 C₂H₅OH + 2 CO2 ALCOHOLIC FERMENTATION EQUATION SUMMARIZATION OF FERMENTATION HTTP://TRC.UCDAVIS.EDU/BIOSCI10V/BIS10V/MEDIA/CH06/FERMENTATION.SWF WHAT ORGANISMS USE LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION? Fermented vegetables Pickles! Lactobacillus bulgaricus – a bacteria Yogurt The sugars in the pickles are converted to lactic acid, preserving the pickle Lactose is fermented by the bacteria to lactic acid, which both thickens the yogurt and restricts the growth of bacteria that poisons the food Humans during anaerobic exercise lactic acid is fermented in muscles where oxygen is depleted makes muscles burn RESOURCES http://www.icr.org/article/172/ http://trc.ucdavis.edu/biosci10v/bis10v/medi a/ch06/fermentation.swf http://www.bio.miami.edu/~cmallery/255/255 atp/mcb8.5.fermentation.jpg