* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Visualizing Biological Pathways
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
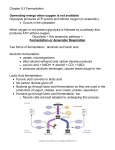
Visualizing Biological Pathways By: Mark Samad and Ben Bispham Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas Pathway • Most common type of glycolysis. Gustav Georg Embden • German physiological chemist. • Conduced studies on the chemistry of carbohydrate metabolism and muscle contraction. • Discovered and linked the steps of the conversion of glycogen into lactic acid. Otto Fritz Meyerhof • Studied medicine at an early age. • Graduated in 1909 and created a work entitled "Contributions to the Psychological Theory of Mental Illness”. • Awarded the Nobel Prize in medicine for his work on muscle metabolism and glycolysis. Jakub Karol Parnas • Major work was the study of the mechanisms of carbohydrate metabolism in muscle tissue. • Discovered the process of phosphorolysis. • Made a major contribution to the theoretical analysis of glycolysis. Prior Knowledge • Louis Pasteur discovered that microorganisms are responsible for fermentation in 1860. • Eduard Buchner discovered that extracts of certain cells can cause fermentation in 1897. • Arthur Harden and William Young determined that a heatsensitive high-molecular-weight subcellular fraction (the enzymes) and a heat-insensitive low-molecular-weight cytoplasm fraction (ADP, ATP and NAD+ and other cofactors). are required together for fermentation to proceed in 1905. Experiment and Results • Experiment 1: Used dissected livers of warm blooded animals and learned of the synthesis of sugar from lactic acid (from reduction of acid), and oxidative deanimation as a way to break down amino acids. Conclusion: Liver is the most important metabolic organ of the body. • Experiment 2: Pressing of muscle tissue to extract fluids. After examining many samples, first major step in glycolysis learned (glucose must be esterfied with phosphate to be broken down further). What Do The Results Mean • Found hexose diphosphate, later named lactacidogen. • Steps of glycolysis were identified by analyzing the products of the reaction. • Lactic acid cycle was found to be undergone in anaerobic environments. References • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gustav_Embden • http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/1922/ meyerhof-bio.html • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Otto_Fritz_Meyerhof • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jakub_Karol_Parnas • http://www.biologyreference.com/Ma-Mo/MetabolismCellular.html