* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cells - Old Saybrook Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
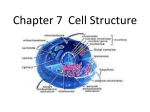
cells Little Bit of Science History Hooke (1665) - used a primitive microscope observing cells for the first time and naming them “cells” Early compound microscope (2 lenses) Hooke’s drawing of cork cells More History Van Leeuwenhoek - 1674 first to use a microscope to look at living cells in pond water and just about anywhere else even the plaque on his teeth! Spirogyra Vorticella And Yet More History Schleiden and Schwann - 1839 Schleiden stated that all plants are made up of cells. Schwann stated that all animals are made up of cells. Virchow - 1857 States that “every cell stems from another cell.” All of that History Gave Rise to the Cell Theory • All living things are made up of cells • All cells come from preexisting cells • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things (take away the order of a cell and the organism will not survive) Types of Cells Eukaryote Prokaryote Prokaryotes ‘Before the Nucleus’ • Archaebacteria and Eubacteria • No nucleus, but all living things have DNA? • Smallest type of cell (0.5-1.5 microns) • No membrane bound organelles • Unicellular / Simpler Prokaryotes don’t have a nucleus ! DNA loosely organized close to the cell membrane Prokaryotes don’t have organelles Organelle - specialized structures within a cell with a specific function, separated by a membrane. But they do have ribosomes, protein factories. Eukaryotes True Nucleus • Have a nucleus where DNA is protected away from the rest of the cell • Have membrane-bound organelles • Larger / more complex • Found in plants, animals, fungi and protists • Most multicellular but some uni- and others are colonial Modern History The Endosymbiotic Theory Lynn Margulis Explanation as to how eukaryotic cells evolved. Margulis' original hypothesis proposed that aerobic bacteria (that require oxygen) were ingested by anaerobic bacteria (poisoned by oxygen), and may each have had a survival advantage as long as they continued their partnership. Cell Parts and Functions Remember this? Cell Membrane All cells have a cell membrane Boundary that allows selected materials to pass through Cell-to-cell recognition receptors made of glycoproteins Gatekeeper/Bouncer Phospholipid Bilayer Cell Wall • Found in plants, fungi, protists and bacteria • Protective support for the organism • Plants made up of CELLULOSE • Porous allows H O, CO , and O 2 through 2 2 Nucleus Directs all cell activities Contains and protects the DNA Includes: Nuclear Envelope Nuclear Pores Nucleolus Chromosomes/ Chromatin Nuclear Envelope Lipid bilayer that protects the DNA from the cytoplasm Nuclear pores allow proteins and RNA to travel into the cytoplasm but prevent DNA from leaving Nuclear envelope is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum Nucleolus Nucleolus Nucleus Made up of protein and RNA Site of ribosome synthesis Cytoplasm (Cytosol) Jelly-like material that surrounds and encases the organelles Many chemical reactions occur in the cytoplasm Mostly made-up of water and enzymes Plastids (plants only) Chloroplast Leucoplast Photosynthetic factory of the cell Storage of starch (polysaccharide) Production of glucose using the energy of sunlight Cells of the potato are filled with leucoplasts Chromoplast Contain pigments such as carotenoids Gives tomatoes their color Ribosomes • Mammalian cell can synthesize 20,000 ribosome subunits per minute • Tiny protein factories, made in the nucleolus then moved into the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum • Made up of 2 subunits Endoplasmic Reticulum 2 Types: Rough and Smooth Rough - ribosomes attached important in protein synthesis, packages new proteins and sends them to the Golgi apparatus Smooth - no ribosomes contains many enzymes that serve different functions; liver cells detoxifies drugs and breaks down glycogen, muscle cells involved in calcium release needed for mus contraction Mitochondria Powerhouse of the cell Contain DNA can replicate independent of the cell Site of cellular respiration Convert chemical energy in food into usable cell energy (ATP) Golgi Apparatus Modifies, collects, packages and distributes molecules Attaches carbohydrates and lipids to proteins Flattened stack of pancakes Lysosomes • Primarily found in animal cells • Small bubble-like • Filled with enzymes necessary for digestion of unneeded cell parts • Recycling center of the cell Vacuoles / Vesicles Vacuole is very large, stores water and sugars for the plant Vesicles are small storage structures that can fuse with membranes to release materials Cytoskeleton 2 Types: Microtubules Microfilaments Microtubules - hollow tubes, support, movement of organelles Framework made of proteins Microfilaments - long, thin fibers, support and movement of cytoplasm Desmosomes Cell snaps - connect cells together and create cell junctions for materials to pass through Centrosomes / Centrioles Centrosomes - area of the cell close to the nucleus where the centrioles are found Centrioles only found in animal cells, used to separate the chromosomes during cell division Chromosomes DNA Tightly coiled chromatin (DNA when the cell is at rest) DNA takes the shape of a chromosome only during cell division