* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8C_BioReview NOTES (7C9)
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
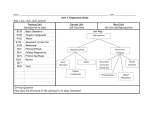
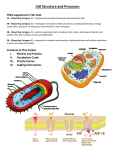
8th Grade – Biology Prep 1. There are two types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. 2. Cell membranes are responsible for controlling what is allowed in or out of the cell. 3. Nuclear membranes are responsible for controlling what is allowed in or out of the nucleus and is one of the last defense mechanisms to protect the nucleus. 4. Cells have a selectively permeable membrane that controls what goes into or out of the cell. 5. Permeable means things are able to pass or travel through the membrane. 6. Selective permeable tells us that only certain things are allowed to pass through the membrane. 7. There are several different ways that something (good or bad) could pass through the membrane and gain access to the cell. 8. There are two categories of transport: passive and active. 9. Passive transport is the movement of substances through a cell membrane without the input of energy. 10. Diffusion is a type of passive transport. 11. Diffusion happens when molecules move away from areas where there are more of them into areas where there are fewer of them. 12. Diffusion stops when the molecules of one substance are spread evenly throughout another substance and equilibrium occurs. 13. The diffusion of water through a cell membrane is called osmosis. 14. In facilitated diffusion, transport proteins help move substances into and out of the cell. 15. Active transport requires energy to move substances through a cell membrane. 16. Endocytosis is the process in which a substance is taken into a cell by surrounding it with the cell membrane, forming a sphere called a vesicle. (taxi!!) 17. Exocytosis is the process in which the membrane of the vesicle fuses with the cell’s membrane and the vesicle’s cargo is released outside the cell. (or the cargo EXITS!) 18. Cells use chemical reactions to change the chemical energy stored in food into forms of energy needed to perform activities or jobs within the cell. 19. Metabolism is the total of all chemical reactions in an organism. 20. The chemical reactions of metabolism require enzymes. 21. Photosynthesis is the process that plants and other organisms use to convert light energy into chemical energy or sugars (like glucose) to be used as food. 22. Chlorophyll and other pigments are used in photosynthesis to capture light energy which is used to produce sugar and oxygen. 23. Producers are organisms that make their own food. (ex. plants and some bacteria) 24. Consumers are organisms that can’t make their own food. (ex. humans, animals, etc) 25. Cellular respiration is the process in which chemical reactions break down food molecules into simpler substances and released stored energy. 26. Cellular respiration of carbohydrates begins in the cytoplasm. 27. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose. 28. Each glucose molecule is broken down into two simpler molecules, releasing energy. 29. Cellular respiration moves into the mitochondria. 30. The two simpler molecules are broken down again, releasing much more energy. 31. This process uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide and water as waste. 32. Fermentation is used by cells that do not have enough oxygen for cellular respiration to release some of the stored energy in glucose molecules. (ex. some bacteria use this) 33. The entire fermentation process occurs in the cytoplasm. 34. The fermentation process produces lactic acid, alcohol, and carbon dioxide as wastes. 35. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are almost the opposite of each other. 36. Photosynthesis produces sugars and oxygen, which are used in cellular respiration. 37. Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide and water, which are used in photosynthesis