* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pg. ___ 4/28 Daily Catalyst
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
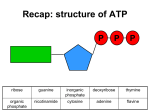
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Pg. ___ 4/28 Daily Catalyst 1) Where in the cell does glycolysis take place? A) B) C) D) Cytosol golgi body nucleus mitochondria 2) Which of the following is not created during glycolysis? A) NADH B) Oxygen C) ATP D) Pyruvate Pg. ___ 4/28 Daily Catalyst 1) A) B) C) D) Where in the cell does glycolysis take place? Cytosol golgi body nucleus mitochondria 2) Which of the following is not created during glycolysis? A) NADH B) Oxygen C) ATP D) Pyruvate Pg. ___ 4/28 Daily Catalyst 1) Where in the cell does glycolysis take place? A) B) C) D) Cytosol golgi body nucleus mitochondria 2) Which of the following is not created during glycolysis? A) NADH B) oxygen C) ATP D) Pyruvate Class Business • Daniel’s Review • Homework due Wednesday • Last full week of school • Bristin be prepared to review tomorrow Cellular Respiration Key Point #1: Glycolysis consists of two major phases. -Energy investment phase -Energy payoff phase Key Point #2: Glycolysis begins with glucose 2 ATP molecules are invested. Need money to make money. 4 ATP molecules are produced. 4-2(energy investment phase)= 2 ATP left! Key Point #3: Glycolysis ends with 2 pyruvate molecules Substrate-level phosphorilation • Key Point #4: Substrate level phosphorylation: • Enzymes transfer a phosphate group from a substrate to ADP • Occurs in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle Classwork: 8 mins Noise Level: 2 In your groups explain how the metabolic processes of cellular respiration and photosynthesis recycle oxygen. Which metabolic process is common to both aerobic cellular respiration and alcoholic fermentation? A) Glycolysis B) Krebs cycle C) Electron transport chain D) Production of proton gradient Which metabolic process is common to both aerobic cellular respiration and alcoholic fermentation? A) Glycolysis B) Krebs cycle C) Electron transport chain D) Production of proton gradient • Which of the following is an important difference between lightdependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis? A) The light-dependent reactions occur only during the day; the lightindependent reactions occur only during the night. B) The light-dependent reactions occur in the cytoplasm; the lightindependent reactions occur in chloroplasts. C) The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and NADPH; the lightindependent reactions use stored energy in ATP and NADPH. D) The light-dependent reactions utilize CO2 and H2O; the lightindependent reactions produce CO2 and H2O. • Which of the following is an important difference between lightdependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis? A) The light-dependent reactions occur only during the day; the lightindependent reactions occur only during the night. B) The light-dependent reactions occur in the cytoplasm; the lightindependent reactions occur in chloroplasts. C) The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and NADPH; the lightindependent reactions use stored energy in ATP and NADPH. D) The light-dependent reactions utilize CO2 and H2O; the lightindependent reactions produce CO2 and H2O. • All of the following occur in cyclic photophosphorylation EXCEPT A) Electrons move along an electron transport chain. B) Electrons in chlorophyll become excited. C) ATP is produced. D) NADPH is produced. • All of the following occur in cyclic photophosphorylation EXCEPT A) Electrons move along an electron transport chain. B) Electrons in chlorophyll become excited. C) ATP is produced. D) NADPH is produced. • . In the process of photosynthesis, the production of ATP is directly linked to which of the following? A) The active transport of protons through ATP synthase from the Stroma to the thylakoid space. B) The reduction of NADP+ to NADPH in the chloroplast. C) The splitting of water in the thylakoid space. D) The diffusion of protons through ATP synthase across the thylakoid membrane. • . In the process of photosynthesis, the production of ATP is directly linked to which of the following? A) The active transport of protons through ATP synthase from the Stroma to the thylakoid space. B) The reduction of NADP+ to NADPH in the chloroplast. C) The splitting of water in the thylakoid space. D) The diffusion of protons through ATP synthase across the thylakoid membrane. • Which of the following incorrectly pairs a metabolic process with its site of occurrence? • A) Glycolysis- cytosol • B) Citric Acid Cycle- mitochondrial membrane • C) ATP Phosphorylation-cytosol and mitochondria • D) Electron Transport Chain- inner mitochondrial membrane • Which of the following incorrectly pairs a metabolic process with its site of occurrence? • A) Glycolysis- cytosol • B) Citric Acid Cycle- mitochondrial membrane • C) ATP Phosphorylation-cytosol and mitochondria • D) Electron Transport Chain- inner mitochondrial membrane • In glucose degradation under aerobic conditions: • A) oxygen is the final electron acceptor • B) oxygen is necessary for ATP synthesis • C) water is produced • D) both (A) and (C) • In glucose degradation under aerobic conditions: • A) oxygen is the final electron acceptor • B) oxygen is necessary for ATP synthesis • C) water is produced • D) both (A) and (C) • In which of the following reactions is the reactant oxidized? • A) FAD-->FADH2 • B) NAD+--> NADH • C) NADPH--> NADP+ • D) ADP--> ATP • In which of the following reactions is the reactant oxidized? • A) FAD-->FADH2 • B) NAD+--> NADH • C) NADPH--> NADP+ • D) ADP--> ATP • In the course of glycolysis: • A) NADH is reduced to NAD+ • B) NAD+ is oxidized to NADH • C) Glucose is degraded into two molecules of pyruvate • D) both (A) and (B) • In the course of glycolysis: • A) NADH is reduced to NAD+ • B) NAD+ is oxidized to NADH • C) Glucose is degraded into two molecules of pyruvate • D) both (A) and (B) • Which of the following correctly describes the amount of ATP produced from the high energy carrier coenzymes? • A) 1 FADH2 --> 1 ATP • B) 1 FADH2 --> 3 ATP • C) 1 NADH --> 1 ATP • D) 1 NADH --> 3 ATP • Which of the following correctly describes the amount of ATP produced from the high energy carrier coenzymes? • A) 1 FADH2 --> 1 ATP • B) 1 FADH2 --> 3 ATP • C) 1 NADH --> 1 ATP • D) 1 NADH --> 3 ATP • Which of the following correctly describes the amount of ATP produced from the high energy carrier coenzymes? • A) 1 FADH2 --> 1 ATP • B) 1 FADH2 --> 3 ATP • C) 1 NADH --> 1 ATP • D) 1 NADH --> 3 ATP • Which of the following correctly describes the amount of ATP produced from the high energy carrier coenzymes? • A) 1 FADH2 --> 1 ATP • B) 1 FADH2 --> 3 ATP • C) 1 NADH --> 1 ATP • D) 1 NADH --> 3 ATP • How many turns of the Calvin cycle are required to produce one molecule of glucose? • A) 1 • B) 2 • C) 3 • D) 6 • How many turns of the Calvin cycle are required to produce one molecule of glucose? • A) 1 • B) 2 • C) 3 • D) 6 • Plants give off oxygen as a waste product of photosynthesis. This oxygen comes from: • A) the Krebs Cycle • B) the Calvin Cycle • C) photolysis • D) photorespiration • Plants give off oxygen as a waste product of photosynthesis. This oxygen comes from: • A) the Krebs Cycle • B) the Calvin Cycle • C) photolysis • D) photorespiration • Which of the following is NOT directly associate with photosystem II? • A) harvesting light energy by chlorophyll • B) release of oxygen • C) splitting of water • D) production of NADPH • Which of the following is NOT directly associate with photosystem II? • A) harvesting light energy by chlorophyll • B) release of oxygen • C) splitting of water • D) production of NADPH • Where in the cell is ATP-Synthase located? • A) in the nuclear membrane • B) in the thylakoid membrane • C) in the cristae membrane of mitochondria • D) both (B) and (C) • Where in the cell is ATP-Synthase located? • A) in the nuclear membrane • B) in the thylakoid membrane • C) in the cristae membrane of mitochondria • D) both (B) and (C) • Which of the following statements about the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis is correct? • A) they provide the carbon that becomes incorporated into sugar • B) They produce PGA, which is converted to glucose by carbon fixation in the light-independent reactions • C) Water is split apart, providing hydrogen ions and electrons to NADP for temporary storage • D) They occur in the Stroma of chloroplasts • Which of the following statements about the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis is correct? • A) they provide the carbon that becomes incorporated into sugar • B) They produce PGA, which is converted to glucose by carbon fixation in the light-independent reactions • C) Water is split apart, providing hydrogen ions and electrons to NADP for temporary storage • D) They occur in the Stroma of chloroplasts • Which of the following is an example of a coupling of an endergonic reaction with an endergonic one? A) Unicellular organisms that live in freshwater, such as amoeba, must pump out excess water using their contractile vacuole B) The enzyme lactase binds with lactose to produce molecules of glucose and galactose C) Electrons escaping from chlorophyll a are replaced by those released by the hydrolysis of water D) The flow of electrons down an electron transport chain in mitochondria powers the pumping of protons against a gradient into the outer compartment • Which of the following is an example of a coupling of an endergonic reaction with an endergonic one? A) Unicellular organisms that live in freshwater, such as amoeba, must pump out excess water using their contractile vacuole B) The enzyme lactase binds with lactose to produce molecules of glucose and galactose C) Electrons escaping from chlorophyll a are replaced by those released by the hydrolysis of water D) The flow of electrons down an electron transport chain in mitochondria powers the pumping of protons against a gradient into the outer compartment • Which of the following statements about cellular respiration is correct? • A) Most CO2 produced during cellular respiration is released form glycolysis • B) Protons are pumped through ATP synthase • C) The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain is NAD+ • D) ATP is formed because an endergonic reaction is coupled with an exergonic reaction • Which of the following statements about cellular respiration is correct? • A) Most CO2 produced during cellular respiration is released form glycolysis • B) Protons are pumped through ATP synthase • C) The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain is NAD+ • D) ATP is formed because an endergonic reaction is coupled with an exergonic reaction • What type of macromolecule (polymer) are enzymes? • A) Polysaccharides • B) Proteins • C) Lipids • D) Nucleic Acids • What type of macromolecule (polymer) are enzymes? • A) Polysaccharides • B) Proteins • C) Lipids • D) Nucleic Acids • Which of the following statements about enzymes is false (not true)? • A) Enzymes are proteins • B) Enzymes speed up reactions • C) Enzymes are not affected by pH and temperature • D) Enzymes lower activation energy (the amount of energy necessary for a reaction to occur) • Which of the following statements about enzymes is false (not true)? • A) Enzymes are proteins • B) Enzymes speed up reactions • C) Enzymes are not affected by pH and temperature • D) Enzymes lower activation energy (the amount of energy necessary for a reaction to occur) • Which of the following environmental factors DOES NOT affect (change) the activity of an enzyme? • A) Temperature • B) pH • C) amount of substrate • D) amount of product • Which of the following environmental factors DOES NOT affect (change) the activity of an enzyme? • A) Temperature • B) pH • C) amount of substrate • D) amount of product