* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NA stabilization
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
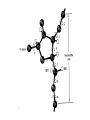
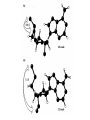
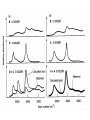
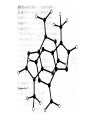
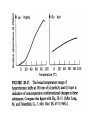
Forces stabilizing Nucleic Acid Structures Sugar –Phosphate chain: Reasonably strain free. Conformationally relaxed arrangement of sugar phosphate backbone in double helices. Glycosidic bonds: syn or anti conformations. Mostly anticonformation Sugar Ring: C2’ endo conformation in B-DNA and C3’ endo in some RNA structures. Base Pairing: Standard Watson Crick base Pairind is most preferred. Other kind of pairings do occur in certain DNA and RNA structures. Watson Crick Base pairs are most stable as demonstrated by Lord and Rich by IR spectroscopy. IR spectrum of N-H bond. But H-bonds do not stabilize DNA structure: DNA is denatured in non-polar solvents (ethanol) which generally stabilize the H-bonding. Base Stacking and hydrophobic interactions: The major force involved in the stabilization of nucleic acid structures. Nucleic acid bases stack in aqueous solution The aggregation of bases can be monitored by measuring their osmotic coefficient (a colligative property) Destabilization of stacking by heating leads to hyperchomism (increase in the absorbance). The unstaking of the single stranded poly A by heat is a noncooperative conformational change The stacking is very specific to the bases and the hydrophobic interactions responsible for this interaction is poorly understood Ionic interaction Stabilization of phosphate groups by cations. Divalent cations like Mg 2+ play significant role in stabilizing the nuclein acis structures.